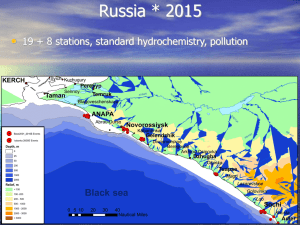
Author: Maxmudova I. “For Whom the Bell Tolls?” • Our environment faces several problems, and many of these seem to be worsening with time, bringing us into a time of a true environmental crisis. It is therefore becoming increasingly important to raise awareness of the existence of these issues, as well as what can be done to reduce their negative impact. Some of the key issues are: • 1) Pollution • Pollution of the air, water and soil caused by toxins such as plastics, heavy metals and nitrates, caused by factors such as toxins and gases released by factories, combustion of fossil fuels, acid rain, oil spill and industrial waste. • 2) Global warming • The emission of greenhouse gases due to human activity causes global warming, which in turn causes an increase in temperature that then leads to rising sea levels, melting of polar ice caps, flash floods and desertification. • 3) Overpopulation • We are facing a shortage of resources such as food, water and fuel to sustain the rising global population, particularly in developing countries. Intensive agriculture attempting to lessen the problem actually leads to more damage through the use of chemical fertilizers, pesticides and insecticides. • 4) Waste disposal • An excessive amount of waste is produced and dumped in the oceans. Nuclear waste is particularly dangerous, as well as plastics and electronic waste. • 5) Ocean acidification • The increase in the production of carbon dioxide by humans causes the oceans’ acidity to rise, which has a negative impact on marine life. • 6) Loss of biodiversity • Species and habitats are becoming extinct due to human activity. This causes an imbalance in natural processes like pollination and poses a threat to ecosystems – coral reef destruction is particularly affected. • 7) Deforestation • Loss of trees in order to make space for residential, industrial or commercial projects means that less oxygen is produced, and temperature and rainfall are affected. • 8) Ozone layer depletion • Pollution caused by chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) in the air creates a hole in the ozone layer, which protects the earth from harmful UV radiation. • 9) Acid rain • Pollutants in the atmosphere such as sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides cause acid rain, which has negative consequences for humans, wildlife and aquatic species. • 10) Public health issues • Lack of clean water is one of the leading environmental problems currently. Pollutants in the air also cause issues such as respiratory disease and cardiovascular disease. Our planet is wonderful, isn’t it? There are many fantastic plants and unique animals and birds. But is it still the world we live in? Who is in charge of it? We will do our project to decide: • Is it possible for us to live without nature? • What way does our lifestyle influence the global environmental changes? • What should we do to save the environment? At this project you will know: • about the difference between ‘ecosystem’ and ‘ecology’ • why the problem of global warming is one of the most urgent • what results deforestation can lead to • what animals are under threat of extinction • about the types of pollution Working with us you will be able to: • to speak English up to the topic • to use the Internet • to make Power Point presentations • to present your work before the audience • to publish your reports Ocean Protection • Marine Protection, Research, and Sanctuaries Act – Extended environmental protection to the oceans. – Requires a permit for dumping wastes and other foreign materials into ocean waters. – Establishes marine sanctuaries in ocean waters and in the Great Lakes and their connecting waters. Oil Spills • Oil Pollution Act of 1990 requires oil industry to adopt procedures and contingency plans. • The Clean Water Act authorizes the U.S. government to clean up oil spills and spills of other hazardous substances in ocean waters. – The government can recover cleanup costs from responsible parties. Toxic Substances • Chemicals used for agricultural, industrial, and mining uses that cause injury to humans, birds, animals, fish, and vegetation. • Key federal laws: – Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act of 1947 (as amended in 1972) – Toxic Substances Control Act of 1976 Hazardous Waste • Hazardous Waste – Solid waste that may cause or significantly contribute to an increase in mortality or serious illness or pose a hazard to human health or the environment if improperly managed • Land Pollution – Pollution of the land that is generally caused by hazardous waste being disposed of in an improper manner Toxic Substances Control Act • Requires manufacturers and processors to test new chemicals to determine their effect on human health and the environment before the EPA will allow them to be marketed. • EPA establishes standards. • Requires stationary sources to control emissions. • EPA can limit or prohibit manufacture and sale, or remove it from commerce.