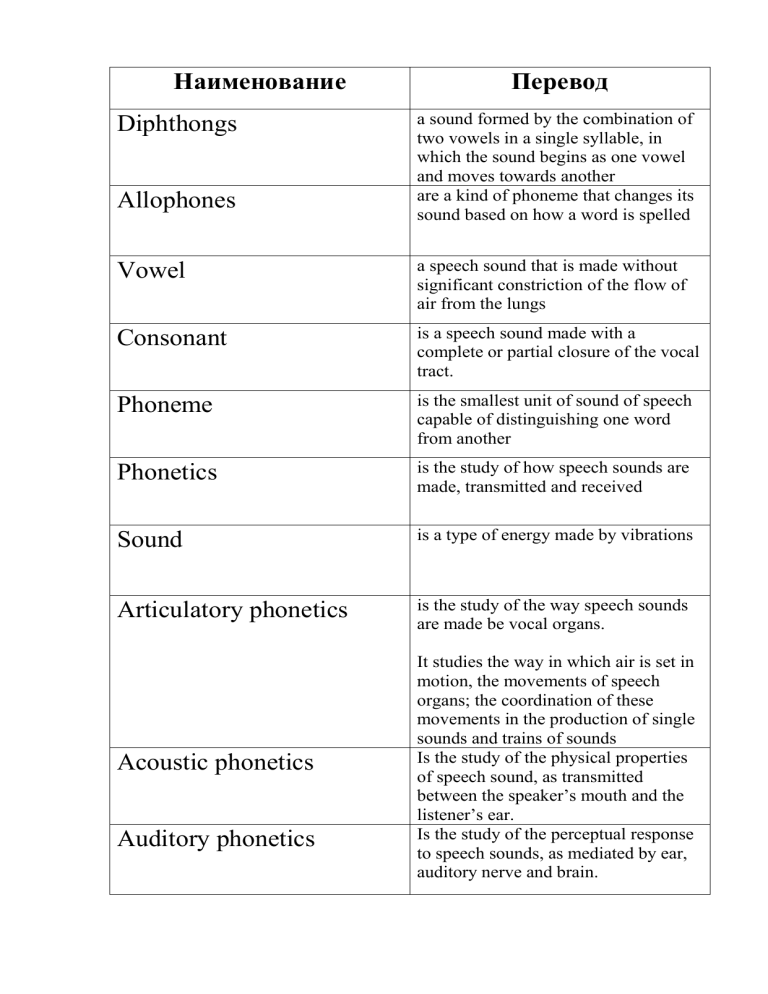
Наименование Diphthongs Allophones Перевод a sound formed by the combination of two vowels in a single syllable, in which the sound begins as one vowel and moves towards another are a kind of phoneme that changes its sound based on how a word is spelled Vowel a speech sound that is made without significant constriction of the flow of air from the lungs Consonant is a speech sound made with a complete or partial closure of the vocal tract. Phoneme is the smallest unit of sound of speech capable of distinguishing one word from another Phonetics is the study of how speech sounds are made, transmitted and received Sound is a type of energy made by vibrations Articulatory phonetics is the study of the way speech sounds are made be vocal organs. Acoustic phonetics It studies the way in which air is set in motion, the movements of speech organs; the coordination of these movements in the production of single sounds and trains of sounds Is the study of the physical properties of speech sound, as transmitted between the speaker’s mouth and the listener’s ear. Is the study of the perceptual response to speech sounds, as mediated by ear, auditory nerve and brain. Auditory phonetics Pitch Intonation Stress Phonology Verbal Acoustics Syllable The sensation of a frequency. A high pitch sound corresponds to a high frequency sound wave and a low pitch sound corresponds to a low frequency sound wave. the rise and fall of the voice in speaking. the way that a word or syllable is pronounced with greater force than other words in the same sentence or other syllables in the same word is the study of those speech sound types and intonation features which have a differential value in the language spoken rather than written is a term referring to the qualities that determine a room's ability to reflect sound waves in such a way as to produce distinct hearing A unit of spoken message larger than a single sound and smaller than a word Distribution of allophones The occurrence of the allophones of a phoneme in different positions in a word coarticulatory/adjustment phenomena A set of methods of joining speech sounds/allophones together in words and at their junctions Syntax the arrangement of words and phrases to create well-formed sentences in a language Alliteration the occurrence of the same letter or sound at the beginning of adjacent or closely connected words Musical tone The auditory impression of periodical waves Noise The auditory impression of nonperiodical waves Articulatory classification Grouping speech sounds according to their major articulatory features Sound loudness is a subjective term describing the strength of the ear's perception of a sound The obstruction of sound occurs when a sound wave travels through a medium to another medium of greater density Assimilation is a sound change in which some phonemes (typically consonants or vowels) change to become more similar to other nearby sounds is the process by which participants in a conversation adjust their accent, diction, or other aspects of language according to the speech style of the other participant is a feature in languages where saying a consonant gives out a puff of air. Accommodation Aspiration Affricate Sonorants a consonant sound that begins as a stop (sound with complete obstruction of the breath stream) and concludes with a fricative (sound with incomplete closure and a sound of friction) are sounds that differ greatly from all other consonants of the language. This is largely due to the fact that in their production the air passage between the two organs of speech is fairly wide, that is much wider than in the production of noise consonants. Nasalization Elision Reductions Omission Linking language is the production of a sound while the velum is lowered, so that some air escapes through the nose during the production of the sound by the mouth. the omission of a sound (a phoneme) in speech. Elision is common in casual conversation. More specifically, elision may refer to the omission of an unstressed vowel, consonant, or syllable. are lost sounds in words, which happens in spoken English. For instance, "going to" changes to "gonna". is the missing of one or more items that must exist in a sentence or utterance. It happens if the lexical item which should be present is omitted or deleted. refers to sentence connectors used to express relationships between ideas and to combine sentences Intervocalically immediately preceded and immediately followed by a vowel Juxtaposition the act or an instance of placing two or more things side by side often to compare or contrast or to create an interesting effect the pronunciation of a sound with greater muscular effort or constriction than is typical Tenseness Prominence stress given to a certain syllable in a word, or to a word in a sentence. Onset is the consonant sound or sounds at the beginning of a syllable, occurring before the nucleus. Monosyllabic consisting of one syllable Lateral release is the release of a plosive consonant into a lateral consonant. Recessive showing a tendency to recede from the end toward the beginning of a word. Prefix is a group of letters that's added to the beginning of a word. Suffix is a letter or group of letters added at the end of a word which makes a new word Compound is a lexeme (less precisely, a word or sign) that consists of more than one stem. Prosody is a complex, formed by significant variations of pitch, loudness, tempo and rhythm Syntagm a linguistic unit consisting of a set of linguistic forms (phonemes, words, or phrases) that are in a sequential relationship to one another. a strongly stressed syllable which is generally the last strongly accented syllable of an intonation pattern and which marks a significant change of pitch direction. is a complete stop of phonation Nucleus Pause Speech Rhythm is traditionally defined as recurrence of stressed syllables at more or less equal intervals of time in a speech continuum Dialect A variant of the language that includes differences in grammar, vocabulary, and pronunciation Accent A dialect includes a way of pronouncing the language Idiolect Individual speech of members of the same language community Diglossia a situation in which two languages (or two varieties of the same language) are used under different conditions within a community, often by the same speakers. The term is usually applied to languages with distinct ‘high’ and ‘low’ (colloquial) varieties, such as Arabic.