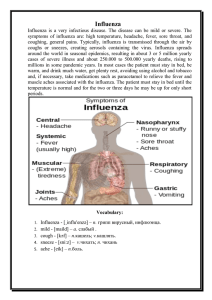
Pharmaceutical care of Common Cold The Common Cold The common cold is a viral infection of the upper respiratory tract Usually last approximately 7 days Associated with a number of viruses – Ex. Rhinoviruses, parainfluenza viruses Season of the year, age, and prior exposure are important factors in the type of virus causing the infection and the type of symptoms that may occur Common Cold Statistics Adults have 2-4 colds per year Children may have up to 10 colds per year How does it spread? Very contagious Spread from person to person Usually from nasal secretions and from fingers of the affected person Most contagious in the first 3 days after symptoms begin Viruses can last up to 5 hours on the skin and hard surfaces Preventing spread of GOOD HANDWASHING! Cough and sneeze into arm or tissue, not into your hand Aerosol sprays (ex. Lysol) Antibacterial sanitizers (ex. Purell) Symptoms Begins with a feeling of dryness and stuffiness in the nasopharynx (nose) Nasal secretions (usually clear and watery) Watery eyes Red and swollen nasal mucous membranes Headache Generalized tiredness Chills (in severe cases) Symptoms cont.. Fever (in severe cases) Exhaustion (in severe cases) If the pharynx and larynx (throat) becomes involved: • • Sore throat Hoarseness Treatment of common cold Antihistamines Decongestants Pain Relievers Cough suppressants Nasal Strips Antibiotics are ineffective!!! Treatment of common cold The Don’ts Second-generation (nonsedating) antihistamines are generally ineffective for common cold symptoms. Intranasal zinc is not recommended; it can cause permanent damage to sense of smell. Echinacea does not appear to reduce a cold’s duration or severity. Antibiotics are contraindicated—colds are viral, not bacterial. Codeine does not reduce coughing. Immune-boosting with vitamins and herbs does not seem to prevent colds. The Common Cold: Red Flags Warranting Referral Temperature over 101 degrees for more than 48 hours A cough with pain in the chest Shortness of breath Persistent sore throat, without a runny or stuffy nose Age <9 months or frail patients of advanced age Serious symptoms unresponsive to OTC medicines, or new symptoms suggesting complications (eg, otitis media, sinusitis, chronic bronchitis, exacerbations of reactive airway disease) See the doctor if… Your throat is very red and it hurts to swallow No improvement within 7 days Severe headache with a fever Worsening pain in one or both ears Any chronic medical condition – Ex. Asthma or diabetes Endnote Colds are costly, with patients spending money on treatment, OTC products, and often, useless antibiotics. Colds are also responsible for millions of days of sick leave at work and school. Pharmacists’ best course of action is to help patients self-treat and make rational choices about OTC products when possible and to refer patients when complications are present.