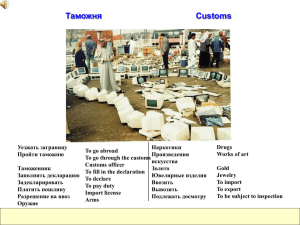
time planning
реклама

The process of project time planning • Irrespective of whether the project manager is developing time, cost or quality plans, the same basic procedure is adopted: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. • evaluate the project through the Statement of Work (SOW); generate a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS); execute Project Logic Evaluation (PLE); separate time, cost and quality planning; use network analysis (CPM or PERT) to generate a Draft Master Schedule (DFM); This process is known as the top-down strategic approach to project planning. The process of project time planning Step 1. The statement of work (SOW) • The statement of work is the descriptive document that defines the overall content and limits of the project. • The SOW includes all the work that has be done in order to complete the project. However, the project cannot be planned or controlled at this level as it is too big. It is necessary to break the whole down into individual components that can be individually evaluated and managed. • A typical SOW contains all the information that is required by a contractor. The level and accuracy of information should be such that contractors or others can price for the work to be carried out. The statement of work (SOW) • Typical SOW contract documents include: – Signature block and project title. – Definition of contract terms and scope. It summarizes the terms and conditions used and describes the range and extent of the works in sufficient details to identify the limits of the project. – Information and facilities to be provided by the client detail the additional obligations of the client. – Project approval requirements. – Terms of payment and interim valuations. – Working drawings. – Specification. – Schedules. Purpose of SOW • The main purpose of a SOW is to define the liabilities, responsibilities and work agreements between clients and service providers. • A well-written SOW will define the scope of the engagement and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for the engagement. • Therefore, the KPIs can be used to determine whether the service provider has met conditions of the SOW and use it as a baseline for future engagements. Purpose of SOW • SOW contains all details of non-specifications requirements of the contractor or service provider's effort. Whenever specifications are involved, the references are made from SOW to specific specification documents. • These specification documents can be functional requirements or non-functional requirements. • Functional requirements define how the software should behave functionally and non-functional requirements detail other characteristics of the software such as performance, security, maintainability, configuration management, etc. Format of SOW 1. Scope • This section describes the work to be done in a technical manner. If the system to be built is a software system, this section defines the hardware and software requirements along with the exact work to be done in terms of the final system. • If there is anything 'out of scope', those areas are also mentioned under a suitable subheading. Format of SOW 2. Location • The location where the work is performed is mentioned under this section. This section also details the hardware and software specifications. In addition to that, a description about human resources and how they work are addressed here. Format of SOW 3. Timelines • This defines the timeline allocated for the projects. It includes the development time, warranty time and maintenance time. In addition to calendar time, the man days (total effort) required to complete the project is also noted. 4. Delivery schedule • This section of the SOW describes the deliveries and the due dates for the deliveries. Format of SOW 5. Standards • The standards (internal or external) are defined in this section. All deliveries and work done should comply with the standards defined in this section of the document. 6. Acceptance Criteria • This section defines the minimum requirements for accepting deliverables. It also describes the criteria used for acceptance. SOW is a critical document for project management. It defines the scope of the work and the work agreements. Therefore, all stakeholders of the project should have a thorough understanding of the SOW of the project and adhere to it. The work breakdown structure (WBS) Level of definition of the WBS • Most WBSs operate down to about six levels, but a project manager should operate within whatever levels are most appropriate. • The number of WBS levels required increases with the size and complexity of the project and is determined by the need to define the tasks at a level where there are manageable and achievable. • Small projects may require as few as three levels, whereas big projects may have up to six or seven levels. • High-risk activities should be further broken down in order to isolate the risk and plan for its mitigation. The work breakdown structure (WBS) • • • • • • Numbering and dividing the WBS A logical and straightforward numbering system is required to ensure that each task is properly coded. Task codes can be used as unique identifiers throughout the project for many purposes, including responsibility allocation, cost allocation, monitoring and reporting. The WBS element codes should be designed so as to accommodate the cost accounting code (CAC) system that in use. Most modern project planning and control software (f.e., the computerized database estimating system package– CDES) automatically generates work element codes as the WBS is generated. The same element code will be used in each part of the system I.e. time, cost and quality planning and control. As with most aspects of planning, there is no unique the only way for preparing a WBS. The dividing of the WBS may be based on work type, responsibility, location, etc. The work breakdown structure (WBS) Numbering the WBS Step 3. Project logic evaluation (PLE) – PLE is the process of taking the WBS work packages that have already been identified and showing the sequence in which they are to be carried out. – For time control, the project manager has to know when each WBS activity is programmed to start and finish. This is a prerequisite for placing orders, committing to delivery dates, resource calculations, etc. – PLE is also required for cost-planning calculations and for quality control. – Often, there are more than one way in which the activity could be carried out. Project logic evaluation (PLE) Resource over-allocation Project logic evaluation (PLE) • In reality, most operations are subjects to some kind of resource limitation. This constraint applies just as much to small projects, such as making a cup of tea, as it does to large complex projects. • The parallel sequence of activities as shown in the previous slide is possible, but not for a single person. The logic-driven sequence shown is therefore dependent on additional resources. • The resource-driven solution is clearly a different layout to the logicdriven solution. Most modern software automatically calculates precedence diagrams using resource-driven or logic driven formats, as input by the user. • Resource over-allocation can be clearly identified by the presentation of a simple bar chart, as shown in the next slide. Project logic evaluation (PLE) Resource over-allocation Step 4. Separate time, cost and quality planning • At this step, the process of planning splits depending upon the aspect being considered: – Project planning from the point of view of time planning and control. Planning techniques applied specifically to time control are known as scheduling. – Cost estimating, planning and control. Basically, the cost planning process consists of isolating individual cost packages and calculating an accurate cost estimate for each one. The individual components are then combined to produce a cost total, usually in the form of budget plan. – Quality planning. Step 5. The Draft Master Schedule • After PLE is in place, the next stage in the planning process is networking and scheduling. • Networking is the process of defining the project logic in terms of the sequence of required activities, and then assigning duration to these activities. This allows the planner to calculate individual start and finish times for each activity and overall project completion date. • Modern software allows networks to be generated quickly and efficiently. More important, it allows complex replanning calculations to be carried out quickly and accurately. • The end result of the scheduling process is the Draft Master Schedule (DMS). The Draft Master Schedule • The DMS is a complete network analysis for the project, showing start and finish time for each activity. • The DMS also identifies the project’s critical path, namely the path through the project that has the longest total activity duration. It is therefore the path of activities that determines the overall project completion date. • Most of the activities will have some leeway (float) as to when they start and finish, but some will not. • Generally, the items without float in their activity windows are critical. Any delay in these activities will delay the following activities, and if the least are on the critical path it will result in overall project completion delay. The Draft Master Schedule • The most obvious uses for a DMS are for: – identifying an overall project completion date; – identifying order and delivery dates for suppliers; – identifying notification and start dates for nominated subcontractors; – identifying key completion dates as a basis for progress planning; – acting as the basis for the implementation risk management system; – identifying logic incompatibilities; – use in cross-checking with subcontractor schedules; – providing the basis for re-planning options and trade-off analysis; The Draft Master Schedule – providing data for the establishment of possible consequences of delay; – providing the data for earned value analysis; – providing data for any necessary resource levelling. • Scheduling involves the following primary stages: – assign durations to each activity; – identify the start and finish window for each activity; – identify those activities with no window (critical path); – re-plan as necessary; – rationalize resources; – form a Draft Master Schedule; – refine the draft to form a Project Master Schedule (PMS). The Draft Master Schedule Gantt chart The Draft Master Schedule Critical Path Method (CPM) The Draft Master Schedule Critical Path Method (CPM) Activities and durations for the bridge project Activity A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O Description Mark out side Dig foundation A Concrete foundation A Cure foundation A Dig foundation B Concrete foundation B Cure foundation B Dig foundation C Concrete foundation C Cure foundation C Erect tower A Erect tower B Erect tower C Erect west span Erect east span Duration (days) 5 3 2 8 6 4 15 4 3 10 1 3 2 5 4 The Draft Master Schedule Critical Path Method (CPM) The Draft Master Schedule Critical Path Method (CPM) The Draft Master Schedule Critical Path Method (CPM) The Draft Master Schedule Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) • • • PERT is a probabilistic approach to project planning which was originally developed in the early 1960s by departments within US Navy, specifically for use on the new ballistic missiles. PERT is event-oriented as it works on calculating the probability of events completed within a given time. The basic steps involved in a PERT analysis are: 1. 2. 3. assign three durations to each activity (optimistic, most likely and pessimistic); calculate activity mean duration and standard deviation; calculate forward and backward pass values;’ The Draft Master Schedule Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) 4. identify those activities with no spare time contained within the duration (critical path); 5. calculate project mean duration and standard deviation; 6. identify target completion date and calculate variance about target; 7. Re-plan as necessary; 8. rationalize resources; 9. form a draft master schedule (DMS); 10. refine the draft to form a project master schedule (PMS). The Draft Master Schedule Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) 1. Assign three durations to each activity. - In PERT calculations, the expected time for an activity is taken as an average of the optimistic, most likely and pessimistic times. This average can also be expressed in terms of an activity standard deviation. - The expected times are used as durations on a standard networking chart and the critical path is then calculated as in standard CPM techniques. - The sum of the individual durations for the critical path can then be used to calculate a project expected time and standard deviation. The Draft Master Schedule Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) 2. Calculate activity mean duration and standard deviation. – PERT durations are based on a beta distribution average. For such a distribution the expected mean time for each activity (a + 4m + b) T= 6 where a = optimistic time, m = most likely time, and b = pessimistic time. – It is to be noted that the beta average give greatest weighting to the most likely outcome. – Standard deviation for each activity S= (b – a) 6 The Draft Master Schedule Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) 3. Calculate forward and backward pass values. This is done in exactly the same way as under the CPM approach using individual activity mean durations. 4. Identify those activities with no spare time contained within the duration (critical path). 5. Calculate project mean duration and standard deviation. Project mean duration = Σ (all individual critical path activity mean durations) Project standard deviation = Σ(all individual critical path activity standard deviations) 2 The Draft Master Schedule Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) 6. Identify target completion date and calculate variance about target. – Either the target duration is given by the client, or the project manager determined it himself, the project manager have to evaluate the probability of this target actually being achieved. – From statistical tables it can be ascertained that the mean duration will be achieved on 50% of occasions. Remember that the beta distribution is not symmetrical. – To calculate the probability of achieving the target completion date the difference between the project mean duration is converted from time (days, weeks, etc.) to standard deviations by standardizing it. This is done by dividing the difference by the project standard deviation. – From statistical tables it can be found the probability of the target date being achieved. The Draft Master Schedule Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) 7. Re-plan as necessary. – PERT replanning is carried out in more or less the same way as in CPM analysis. – Replanning in PERT involves recalculating the average and standard deviation for each activity on the critical path each time the analysis takes place. – Changes in critical path activity mean duration and standard deviation results in changes in the project mean duration and standard deviation. 8. Rationalize resources. 9. Form a draft master schedule. 10. Refine the draft to form a project master schedule. The steps 8, 9 and 10 are carried out in the same way as in CPM analysis. Project re-planning • As soon as the DMS and PMS have been established, things immediately begin to change. • Change is a significant part of any project, and the planning and control system has to be flexible enough to allow for and incorporate change accurately. • Project management is about optimizing time, cost and quality performance, which are intrinsically linked. Changes in requirements of these variables frequently occur, and the project manager has to be able to re-plan the project accordingly. • In practice, the most common requirement for project re-planning calculations concerns time and cost. Clients often ask for projects to be speeded up and need to know how much of an increase in speed is possible and what it will cost. Project re-planning Crash analysis • In crash analysis, the project manager offers re-planning advice based on the relationships between time and cost. This of course assumes that performance or quality criteria are fixed, as is the case in most projects. • Generally, a project will have clearly defined time and cost performance at the start. This will usually be the time and cost limits that were established as part of the statement of works and that have been translated into contractual terms and conditions. • The project could move to a different position in terms of time and cost characteristics. • If we assume that quality is fixed, then cost can be considered as a function of time. Project re-planning Crash analysis Typical time-cost curve Project re-planning Crash analysis • Generally, a time-cost curve will typically have a starting point at the agreed tender or project price. This usually represents the minimum or near-minimum cost value and the near-optimum time value. • In order to save time on the project, there will almost certainly be a requirement to increase resources. This will allow the project to finish more quickly but will result in a cost increase. • If a project manager is looking for ways to achieve this, the most obvious way is to find out which activity can be speeded up at least cost, and then crash that one first, followed by the next cheapest, and so on. This will result in the typical negative time-cost curve. Project re-planning Crash analysis • This curve will rich a point where all critical-path activities have been speeded up as far as possible. • Beyond this point, no further time can be saved on the project. Any further crashing will result in cost increase, and no further time will be saved. • There is no point in crashing any non-critical activities, as this will simply increase costs while giving no time saving. • As critical path items are crashed, the overall length of the critical path will reduce.In most cases, this means that at some point the original critical path will no longer be critical. It is therefore important that the critical path is checked after each crash to ensure that it is still critical. Project re-planning Crash analysis • If a parallel path becomes critical before the crash limit has been reached, then the process has to be repeated so that a new critical path can be identified. • In some cases, two critical paths may appear. It now becomes necessary to crash both critical paths at the same time. This involves identifying those activities on each critical path that have the lowest cost of crashing per unit time and then crashing them simultaneously. • Once any critical path becomes fully crashed, that is the end of the process. • The classical time-cost curve is one example of a trade-off analysis which is widely used in project management. Trade-off analysis Methodology for trade-off analysis 1. Identify the reason for the problem. Trade-offs can occur both before and during the execution of the project. Typical reasons for pre-execution trade-offs are: – changes in client requirements (particularly changes in the required scope of work and cost limits); – discovered design incompatibilities; – changes imposed by subcontractors and suppliers; – misunderstanding resulting from pure communications; – unforeseen problems such as sudden non-availability of important materials; – Changes in organizational strategic objectives (generally resulting from external imposed change) Trade-off analysis Methodology for trade-off analysis • Typical reasons for execution trade-offs: – changes in client requirements (particularly additional required work); – discovered human error (such as inaccurate time estimating); – discovered execution problems (such as unforeseen work complications); – emerging risk (such as inaccurately assessed risk); – project-specific events (such as mechanical failure or unforeseen conditions). • It is imperative that the reason for the problem is identified and some kind of control system put in place to avoid or control the occurrence of the same problem in future. Trade-off analysis Methodology for trade-off analysis 2. Reevaluate the project objectives. Imposed change may result from changes in the project status and environment. – Typical reasons for a relative change in project status resulting from a change in organizational strategy include: – – – – – – – changes in competitor behavior; changes in customer demand; changes in the national and global economy; changes in strategic leadership and emphasis; changes in available technology; the introduction of new codes of practice; the introduction of new legislation. Any of these changes could result in the formulation of new strategic objectives, which in turn result in the original project objectives becoming misaligned. Trade-off analysis Methodology for trade-off analysis 3. Allow for any other relevant factors. Typical examples include: – – – – – – – a deterioration in industrials relations within the company; weather conditions (where relevant); exchange rates (where relevant); mechanical failure and breakdown; discovered errors or omissions in the contract documentation; resource availability problems; consultant problems. 4. Assemble a shortlist of solution scenarios. 5. Select and test the best alternative. 6. Implement the best (or approved) alternative. The PCCS planning cycle Developing estimate accuracy The PCCS planning cycle Project estimating • Cost estimations are prepared first and foremost to calculate the sales price, but they are generally needed on all projects to provide valuable input into a whole host of other management activities: – – – – – – – milestone planning; valuing the likely cost of change notices and variation orders; periodically reviewing the likely final account total; assisting in cost control; assisting in trade-off analysis; assisting in performance monitoring; assisting in establishing productivity targets as a basis for bonus payments. Project estimating Top-down estimating • Top-down estimating is very common and involves senior management setting the overall project budget. They do this by estimating the overall project costs on the basis of their experience, knowledge and accessible project data. • These estimates are often fixed and then handed down to lower-level managers to break down the costs to individual activity and work packages level. • The benefits of top-down estimating: – the budget is set by senior management and is therefore compatible with the overall strategic objectives of the organization; – the budget carries more authority since it originates from senior management; – the budget is less likely to be changed or tampered with during the course of the project; – any such changes are likely to be formalized; Project estimating Top-down estimating – because the estimate originates from higher levels within the organization, it is likely to be more reliable and accurate; – local influence and bias are unlikely to be factors. • The disadvantages are that: – the project team may feel that unrealistic budgets have been imposed upon them; – where great incompatibilities are perceived there may be a reduction in project team motivation; – the senior management may be “out of touch” with operational costs; – politics may be a factor. Some element or package managers may receive a greater budget for “specially” reasons. – the inappropriate budget allocation can affect the entire cost control and performance management systems. Project estimating Bottom-up estimating • The project budget being developed upwards from the individual activity level. • Each activity is estimated as accurately as possible in terms of labor hours, materials and equipment required to complete the task. • These estimates are then converted into a financial cost estimate. • The resulting tusk budgets are then aggregated to give the total direct costs of the project. • The project manager or senior manager will then add indirect costs, any contingencies and a profit figure, to arrive at the total project budget. Project estimating Bottom-up estimating • The advantages of the bottom-up estimating are that: – the people “on the ground” decide on what is required and on how much it should cost; – the people are more likely to commit themselves when they have had a say in setting their own budgets; – the people who set their own budgets are more likely to stick to them; – provided budgets are allocated fairly, this eliminates the motivational problems associated with favouritism or other forms of inequitable budget allocation. • The disadvantages are that: – the budgets may carry less status than those set by senior management; Project estimating Bottom-up estimating – careful controls are needed to ensure that budgets are not altered; – local influence and bias may be issues; – it may be difficult to adjust budgets in line with strategic changes; – the budgets are more easily overridden by senior management; – senior managers sometimes feel threatened; – element and package managers tend to overestimate to “be on the safe side”; – the whole project budget can become driven by the process itself rather than by market conditions. Project estimating Iterative estimating • Iterative estimating is based on negotiation and represents a compromise between top-down and bottom-up estimating. • Element and package managers develop detailed action plans and corresponding estimates for the work which they are responsible for. They then present these plans and estimates to senior management for approval. • Operational managers and senior managers negotiate on the action plans and estimates, and some re-definition and refining occur. • The end result should be an action plan and estimate that lies somewhere between the market-driven conservative estimate of the senior management and the process-driven generous estimate of the operational manager. Project estimating Iterative estimating • Advantages of the iterative estimating: – the estimate is prepared by the operational manager; – the estimate is tempered by senior management and is therefore more likely to be compatible with the strategic objectives of the organization; – the influence of market forces is maintained; – the end result combines practical (operational) considerations with senior management (strategic) considerations. • Disadvantages: – the negotiation process is time consuming and costly; – adequate control procedures have to be put in place to prevent the senior managers simply overriding the operational managers; – some operational managers might be better at negotiation than others and may secure themselves a better budget total than their less gifted colleagues; – negotiation skills can become more important than estimating skills. Project estimating Bidding strategy and estimate reporting • • In the case of an internal project management system, once the project or work package has been approved in principle, the next stage is to prepare the bid for approval by senior management. In most cases, the developing of the bid progresses to eight stages: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Formulate a viable estimating strategy. Make initial (order of magnitude) minimum realistic estimate. Carry out any necessary preliminary refinement. Make realistic (indicative) minimum estimate. Add for profit and risk. Compare overall price to projected cost limit. Make subjective evaluation of bid success probability. Develop final (definitive) estimate. Project estimating Computerized database estimating systems (CDES) • The CDES works by linking together several different databases. Each database contains a different type of information: – The description library. It is a collection of standard descriptions. The descriptions are arranged in an hierarchical format, where each item of work is broken down into more and more detail until a level of detail is arrived at where accurate pricing can occur. Different databases are available for different industries. – The price code and unit rate databases. For each description, the price code database has a record of what individual components are included within the description. For every library description, there is pre-set list of labour, equipment and material, together with time allowances and unit costs. – Other database elements. Computerized database estimating systems • Computerized database estimating systems (CDES) are used during the estimate measurement process. • In manufacturing/engineering/construction projects, drawing information is transcribed directly into the CDES either by manual measurement or by scanning directly from drawings using a digitizer. The CDES then stores an electronic version of the drawing data and builds up an automatic electronic budget plan. Финансовый план проекта Цели финансового планирования: обеспечение ликвидности, т.е. способности очередные платежи производить без задержек; обеспечение (например, чтобы замораживались; экономичности финансовые финансирования, средства излишне сохранение финансовой независимости по отношению к контрагентам, поставщикам и другим внешним организациям. не Финансовый план проекта Основой для составления плана платежей обычно является план издержек, однако необходимо учитывать, что только часть платежей совпадает по сумме и времени с издержками. При внешних проектах особое значение имеет характер соглашения о платежах. Чем больше размер аванса и чем чаще осуществляется оплата за выполненные объемы работ, тем у исполнителя меньше проблем с сохранением ликвидности и меньше риск в случае прекращения проекта. Необходимые сведения о финансировании, планировании и учете издержек в форме, хорошо понятной и для непрофессионалов приводятся в книге профессора А. Шваба «Менеджмент для инженеров». The project budget plan • The project budget is the end result of the planning phase. It is the sum total of all individual work package budgets for the whole project. • The project budget is therefore the estimated cost for the whole project. It comprises a whole series of sub-budgets for individual WBS work packages. The project budget WBS is normally identical to the project WBS that is developed during the planning phase of the project life cycle. It is developed to a level where a pre-tender cost check is performed before contract documents are issued to prospective tenderers. • The project budget is not the same as the selling price, or even the tender price. The project budget is the effective cost limit as authorized and set by the client. • The final or baseline budget plan are the end result of a series of internal estimate planning processes, tempered by the external influences of tenderers who are usually free to price the same works in any way that they wish. The project budget plan The project budget plan • At it most basic level, the project budget relates the forecast costs to particular project task. It also considered to be a management, planning and decision-making tool, that may be used for: – establishing the overall budget baseline for the project. This baseline acts as the basis for subsequent earned value analysis; – developing (in association with the project schedule) the projected cost curves for each element and work package; – establishing a reference for variance analysis allowing the performance of individual elements and packages to be assessed throughout the course of the project; – moderating the spending of element and package managers; – generating the basic data for scenario analysis in trade-offs; – estimating the likely effects of change notices and variation orders. The project budget plan Budget development and layout • To be an effective management tool, the project budget should contain at least: – project objectives and activities in terms of measurable outputs; – the financial resources allocated to achieve these objectives and complete the activities; – clearly defined start and finish points of each activity; – the facility to compare actual and planned performance details. • Perhaps the most important aspect of the budget is the cost-coding format. For accurate monitoring and control, it is essential that each element of the budget corresponds to an identifiable and measurable work package and that the budget element and its associated work package must share a common, unique cost code. The project budget plan Budget development and layout Budget development and layout The project budget plan Budget development and layout • Preliminary costs are those that are considered to be general project overheads. • Prime cost sums are those where the work is to be subject to a nominated or named subcontractor. • Provisional sums are those where the exact extent of the works is not known and an exact cost estimate cannot be produced. A provisional sum is included to cover the likely extent of the works. • Direct payments are payments made through the project, but made to organizations that are not part of the actual project team. • Dayworks are generally included to allow for unforeseen and unmeasurable works, which might nevertheless arise. • Typical overall additions would include allowances for contingencies, fees and taxes. Budget development and layout Budget development and layout The project budget plan Budget development and layout • The final requirement for completion of the baseline budget plan is to calculate some form of expenditure profile for the project. This is normally performed by relating the CAC sums to the project draft master schedule (DMS). • Modern project planning and control software does this automatically. • The start and finish dates for each activity are used to show the start and the finish expenditure dates for each CAC element. By knowing the spend duration and the spend curve characteristics of each activity, it is possible to calculate a spend profile for each package and for rollup elements at each level higher in the WBS. The project budget plan Budget development and layout The project budget plan Budget changes • Budgets are generally not static, particularly in large projects where the exact scope of work is difficult to define precisely at the outset. They change throughout the life cycle of the project, and with every agreed project-scope variation (or change order) there is an associated variation in cost that has to be budgeted for. The budget should therefore be prepared in a manner in which changes are easy to accommodate. • At any time during a project, its budget should be transparent enough to identify the original budget, the cost associated with approved change orders, and the total current budget. • It is clearly important that budget changes are controlled in some way. Large project typically include some kind of change control section (CCS). The CCS is responsible for monitoring all change on the project and for predicting the implications of change requests before authorizing them. • On large projects, changes to the project budget are often formalized through the issue of a cost account variation notice (CAVN). The project budget plan • Most changes to project budgets are necessitated by the issue of change notices. These are variation orders that are issued by the project manager or design team members. The effect of the change notice is a modification of the project’s work requirements. This may be necessary for a number of reasons. The most obvious ones are work items that have been overlooked during the design stage, unforeseen complications and additional works, and changes in client preferences and requirements. • Change orders often provide an excellent opportunity for the contractors and suppliers to make a healthy profit. The project team is “locked in” and the selling price for a change order is not normally constrained by normal market forces. Often, but most particularly when work is scarce, companies will take on projects at little or no profit margin, in the hope that there will be scope changes during project execution period where they can increase the sales price and realize a healthy return. Однопроектное сравнение Сравнительный расчет издержек Виды издержек Проект: внедрение программы 1С Существующая система, руб Запланированная система, руб. Издержки на персонал Капитальные затраты Материалы Услуги Прочие Суммарные издержки 400.000 95.000 5.000 86.000 94.000 10.000 70.000 10.000 Уменьшение издержек Компенсация издержек проекта (3 года) Издержки на внедрение Снижение издержек за 1 год 500.000 270.000 230.000 70.000 60.000 100.000 Снижение издержек в последующие годы 160.000 Многопроектное сравнение Проекты Складирование Механическое измельчение Электродинамическое измельчение Снижение издержек за три года, руб. 420.000 560.000 700.000 Трудозатраты на проект (чел. Х мес.) 8 12 16 Экономия издержек на единицу трудозатрат (руб./чел.Хмес.) 52.500 46.700 43.700 Издержки на персонал проекта (руб./чел.Хмес.) 12.000 11.000 13.500 4,38 4,24 3,24 4 6 12 66.670 80.000 0 Срок окупаемости в месяцах 8,6 8,5 11,0 Время до получения чистого эффекта, месяцев 12,6 14,5 23,0 Параметры Экономия издержек на рубль издержек на персонал (руб.) Длительность проекта в месяцах Экономия издержек в текущем году Перепланирование проекта • Как только первичное планирование заканчивается (а часто и ранее), ситуация начинает меняться. • Изменения являются характерной чертой проектов, поэтому система их планирования и контроля должна быть гибкой, чтобы адекватно учитывать изменения. • Управление проектом предусматривает оптимизацию соотношения времени, стоимости и качества. Требования по изменению одной из этих переменных возникают часто и руководитель проекта должен быть в состоянии оперативно перепланировать проект. • Заказчики часто просят ускорить ход проекта. Необходимо показать им насколько это возможно и сколько это стоит. Анализ сжатия проекта (Crash Analysis) Издержки Точки сжатия работ критического пути Точка оптимума (минимальный срок и минимальные издержки) Время 0 Управление проектом/контроллинг проекта . Задачи контроллинга Понятие «контроллинг» происходит от английского «to control», что означает управлять, распоряжаться, контролировать, регулировать, проверять, настраивать, обусловливать, нормировать. Задачи контроллинга явно выходят за пределы чистого контроля. Контроллинг должен обеспечить достижение цели проекта. Взаимосвязи планирования и контроллинга проекта Руководство проекта Постановка задач Коммуникация Укаазания, решения Доклад Планирование проекта План хода работ Ресурсный план План времени План издержек Ход работ с обратными связями и корректировками Выполнение проекта Контроллинг Задача сравнения планового и фактического состояния дел Задача контроллинга - зафиксировать отклонения в сроках, издержках, мощностях и ходе выполнения проекта путем сравнения планового и фактического состояния дел и привлечь внимание руководства проекта к необходимости принять необходимые встречные меры или откорректировать планы. Для сравнения фактического и планового состояния дел и установления отклонений важно, чтобы фактическое состояние могло быть четко приурочено к определенному моменту времени. В противном случае можно прийти к ошибочным выводам. Далее производится анализ причин отклонений и выясняется повлияют ли эти причины на дальнейший ход проекта. Центр тяжести анализа причин отклонений ориентирован на будущее проекта и его цели и меньше всего является средством для поиска виновников. Контур регулирования контроллинга проекта Цели проекта Плановые значения Обратная связь Планирование Контроллинг проекта Сравнение плана и факта Анализ отклонений Фактические значения Решния о корректировках Мероприятия Выполнение Внутренние и внешние помехи Контроль над ходом проекта и над временем Власть и деньги, успех, революция, Слава, месть и любви осязаемость – Все мечты обо что-нибудь бьются, и больнее всего – о сбываемость. И. Губерман Чтобы приходить к верным заключениям должна быть создана надежная система обратной связи, которая позволяет получать правдивую, полную и оперативную информацию о состоянии дел; • должно постоянно осуществляться сравнение планового (с учетом ранее проведенных корректировок плана) и фактического состояния дел; • должен быть проведен анализ отклонений. Сравнение планового и фактического состояния работ на определенный день Работ ы 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Сосотояние выполнения = Работа ыполнена Контрольный срок = Работа еще не выполнена 28 29 Анализ тренда вех Вехи представляют собой показатели для краткосрочных целей, упрощающих измерение продвижения (достижений) проекта на протяжении всего периода его выполнения, а не только в конце его. Они указывают также на время, когда могут приниматься решения. Анализ тренда вех показывает в данный момент времени прогноз сроков окончания отдельных работ. Пример: На следующем слайде для обоих рабочих пакетов 1 и 2 в таблице приведены для различных моментов времени сообщения о том, когда они могут быть закончены, исходя из представлений на текущий момент. Далее для наглядности информация представляется графически в виде кривой, начиная с начального момента времени и по ходу работ отражается новая информация. Это позволяет в каждый текущий момент времени видеть состояние работ. Анализ тренда вех Текущий момент времени Рабочий пакет 1 Рабочий пакет 2 Январь “в сентябре” „в мае“ Март „в октябре“ (отставание 1 месяц) „в июне“ (отставание1 месяц) Апрель (без изменений) „в мае“ (1 месяц наверстали) Май „все-таки в сентябре“ (1 месяц наверстали) „срок выдержан в соответствии с планом“ Июль „в ноябре“ (отставание2 месяца) - Август „в октябре“ (1 месяц наверстали) - Сентябрь „в ноябре“ (отставание2 месяца) - Ноябрь „работа выполнена с двухмесячным отставанием“ - Анализ тренда вех Развитие проекта Месяцы Я Ф M A M И И A С O Н Д Декабрь Ноябрь Октябрь Рабочий пакет 1 Сентябрь Август Июль Плановые сроки Июнь Май Апрель Март Февраль Январь Рабочий пакет 2 Контроль издержек Составляющие контроля издержек: -система обратной связи, позволяющая зафиксировать фактическое состояние дел, - сравнение фактического состояния с плановым, - анализ отклонений. Реалистичный контроль издержек возможен только в том случае, если регистрация фактических издержек осуществляется в соответствии с их плановой классификацией. Для этого нужно на стадии планирования рассматривать отдельные рабочие пакеты как носители издержек нижнего уровня. В этом случае они несут в себе не только сроки, но и затраты материальных и человеческих ресурсов, оценка которых дает и соответствующие им издержки. Контроль издержек Составляющие контроля издержек: • система обратной связи, позволяющая зафиксировать фактическое состояние дел, • сравнение фактического состояния с плановым, • анализ отклонений. Реалистичный контроль издержек возможен только в том случае, если регистрация фактических издержек осуществляется в соответствии с их плановой классификацией. Для этого нужно на стадии планирования рассматривать отдельные рабочие пакеты как носители издержек нижнего уровня. В этом случае они несут в себе не только сроки, но и затраты материальных и человеческих ресурсов, оценка которых дает и соответствующие им издержки. Методы сопоставления плановых и фактических издержек • абсолютное сравнение (сравнивают отдельные фактические издержки с плановыми), • сравнение, коррелированное с затратами (сравнивают накопленные фактические издержки с накопленными плановыми издержками ), • сравнение с учетом ожидаемых издержек сравниваются полные (за весь период проекта) плановые издержки с суммой зафиксированных фактических издержек по состоянию на контрольный день, отложенных издержек и ожидаемых плановых издержек. Сравнение плановых и фактических издержек с учетом ожидаемых будущих плановых издержек Вид издержек Издержки Полные издержки (2+3+4) Плановые издержки Фактические Отложенные Ожида емые 1 2 3 4 5 Материалы 350 320 40 - 360 Песонал 300 180 60 80 320 Средства труда 150 100 30 15 145 Прочие 50 50 5 10 65 Всего 850 650 135 105 890 Превышение сроков и издержек в проектах Значительные превышения сроков и издержек в проектах это явления, которые известны уже тысячелетия. Д. Элтон и Ю. Рой пишут: «Сколько проектов в вашей организации были завершены вовремя и уложились в бюджет? Большинство менеджеров ответят вам – ни один. И это вопреки использованию программных инструментов управления проектами, технологии менеджмента, систем управления данными, программ тренинга команд и использованию «лучшего опыта». Каждый менеджер имеет оправдания, почему данный проект удался плохо, но попытки предусмотреть впредь неожиданные проблемы редко имеют успех». Классическим примером является здание оперы в Сиднее, где издержки на строительство превысили смету в 16 раз. Превышение сроков и издержек в проектах Особенно ярко проявляется этот эффект в проектах внедрения информационных технологий. При этом проблемы остаются нераспознанными в течение длительного времени. Так в 1992 г. Социальный департамент Калифорнии начал проект создания автоматизированной системы штата по поддержке детей. Был заключен контракт с фирмой на $75,5 млн. на три года. К 1995 г. расходы незавершенного проекта достигли $260 миллионов. Проект был все же продолжен и только в 1997 году он был прекращен после пятилетней работы. При этом общие издержки достигли $345 миллионов. Меры для улучшения положения с соблюдением издержек и сроков проектов • совершенствование методов оценки, • развитие современных процедур оценки, при которых назывались бы не только конечный срок и расчетная суммарная стоимость, но и представлялась бы соответствующая детализация, а также информация о степени достоверности и качестве единичных оценок, • улучшение качества менеджмента. Существенным шагом в этом направлении является строгое соблюдение последовательности выполнения проекта в соответствии с принятыми фазами проекта. Результаты исследование причин нарушения плановых сроков и издержек Источник и год исследований Число и характер проектов Перерасход средств, % Основные причины General Accounting Office, 1979 940 американских гражданских и военных проектов 75 Инфляция, изменения в проекте, срывы графиков работ, неточные сметы То же, 1982 444 американских гражданских и военных проектов 140 То же Мировой банк, 1980 1014 гражданских проектов во многих странах 30-40 Canaday, 1980 35 американских атомных электростанций 58-408 Инфляция, инновации, сложность, безответственность местных властей Инфляция, увеличение требований безопасности, увеличение ставок банковского кредита Превышение издержек по некоторым крупным германским проектам Проект Издержки в миллионах DM плановые фактические превышение,% Олимпийское строительство 500/67 2000/72 300 Проект реактора THTR 300 710/72 4300/82 506 Проект реактора SNR 300 1700/72 6500/82 282 15/70 35/79 133 Истребитель «Торнадо» (в расчете на один самолет) Примечание: в знаменателе указан год, к которому приведены цены. Проблема оценки истинного состояния проекта в отношении издержек и выполненного объема работ • В больших проектах несинхронность оплаты и выполнения работ может сильно искажать оценку истинного состояния проекта (по стоимости и срокам). • Одним из методов оценки истинного состояния проекта является метод анализа заработанной стоимости. • Однако и он не может учесть всего многообразия причин задержки и опережения платежей по сравнению с выполненным объемом работ, но может служить предупредительным сигналом для проведения более детального анализа. The PCCS operating cycle • The operating cycle, sometimes referred to as the cost and control system, is the section of the PCCS that implements the estimating and budgeting sections of the planning cycle. • The operating cycle authorizes commencement of the priced works and monitors the actual expenditure against planned expenditure in order to generate cost variances. • The PCCS operating cycle comprises four phases: – – – – Phase 2: work initiation; Phase 3: cost data collection; Phase 4: generation of variances; Phase 5: cost reporting. The PCCS operating cycle Phase 2: work initiation • In order to be able to control costs, there must be some form of controlled release of work. • This could be done through the formal issue of a contract, or through control change control notices such as variation orders or works orders. • The project works order (PWO) would typically describe the work, and any standards to be adhered to, and identify the cost center to be charged. This is usually done through some system of cost accounting codes (CAC). The cost accounting codes system is usually based on the project WBS. The PCCS operating cycle Phase 3: cost data collection • PCCS cost-data collection and reporting use earned value analysis (EVA). EVA is simply a way of comparing actual with target figures for performance and cost. • EVA uses variance analysis as the basis for its calculation. Variance analysis is centered on two variances, cost variance and schedule variance. • EVA is based historically on milestone monitoring. A milestone represents a definite stage in the project and is an appropriate point at which to measure performance. • Milestone monitoring is most suitable for use when plans and schedules are not particularly detailed. It is a simple tool, but as with any simple technique, it does have a number of disadvantages. The PCCS operating cycle Phase 3: cost data collection The PCCS operating cycle Phase 3: cost data collection The PCCS operating cycle Phase 3: cost data collection • Milestone monitoring has a number of disadvantages: – Reaction time lag. A milestone report could indicate a cost variance that originated in an element several months previously and it could be to late to fully correct whatever caused the variance. – Residual accumulated overspend. Even if the ongoing expenditure are brought back into line, the accumulated over spend will remain. – Re-planning issues. Milestone programs are very susceptible to re-planning and trade-offs. – Time scale issues. Milestones represent conditions at a particular point in time rather than along a time continuum. This is a limitation as the project is dynamic. Milestones do not allow for work in progress. The PCCS operating cycle Phase 3: cost data collection • EVA is a type of milestone monitoring applied specifically to determine cost and schedule variances for component sections of a project. EVA is an attractive method of project control because it: – is dynamic; – provides combined and simultaneous time- and costperformance assessment; – provides frequent reporting; a good system allows daily reporting, if required; – demonstrates value as well as cost. It therefore gives a high frequency report on profitability; – generates accurate assessment of the cost implication of delays; – allows easier trade-off analysis in that the calculations include resource implications. The PCCS operating cycle Phase 3: cost data collection • The cost variance is the difference between the budgeted cost of the works and the actual cost. For both budgeted and actual costs, the value is taken in terms of the works actually completed or performed. • Variances can be expressed in terms of measurable effort and support effort. • Measurable effort relates to separate elements of work that are set within a defined schedule for accomplishment. Completion of the effort produces tangible results. • Support effort relates to project actions where it is difficult to isolate it into measurable units. Examples would include project support and administrative services. • Variance analysis is designed to show how different parts of the budget plan are performing at any one time. The PCCS operating cycle Phase 3: cost data collection • There are seven major considerations involved in variance analysis: – – – – – Identify and validate the variance. Quantify the variance. Determine the source of the variance. Determine the impact of the variance on the project as a whole. Determine the impact of the variance on other elements and packages. – Determine the extent to which tactical response is already underway. – Determine the range of possible outcomes of any corrective action. The PCCS operating cycle Phase 3: cost data collection Example of variance analysis The PCCS operating cycle • On the tasks that are 100% complete, the earned value is equal to the original budget, irrespective of the costs actually incurred on that task. If Task A in our example is complete, then the earned value of the work done on Task A is $5100 despite the fact that $5200 was spent in achieving this earned value. • The table shows that the project is ahead of budget, but the position is a little better, because the $700 over budget include some work done on the Task G, that was not foreseen at the end of month 3. The PCCS operating cycle Phase 3: cost data collection • Earned value analysis makes use of following variables: – Actual cost of the works performed (ACWP); – Budgeted cost of the works performed (BCWP)/ (actual earned value); – Budgeted cost of the works scheduled (BCWS) /(planned earned value); – Scheduled time for work performed (STWP); – Actual time for work performed (ATWP); – Cost variance (CV); – Schedule variance (SV); – Budget at completion (BAC) /(project baseline); – Estimate at completion (EAC); – Variance at completion (VAC). The PCCS operating cycle Phase 3: cost data collection The PCCS operating cycle Phase 3: cost data collection Estimate at completion (EAC). – The estimate at completion is the estimated total cost of the project. It is the sum of all direct and indirect costs to date plus authorized work remaining: EAC = ACWP + estimate to complete (ETC), and this is the updated estimate of the total project cost. – This approach is sometimes known as the planned estimate approach. The planned estimate approach is simplistic in that it assumes that the current underspend or overspend will continue for the remainder of the project. – The EAC can also be expressed in terms of the budget at completion: EAC = BAC – CV. – EAC can also be expressed in terms of the cost variance index (CVI): EAC = (ACWP/BCWP) x BAC – This approach is sometimes referred to as the current estimate approach. It is less simplistic than the planned estimate approach as it uses BAC rather than EAC. As such it includes an estimated value for the anticipated remaining work content rather than the original estimate of the cost to complete the remaining work. The PCCS operating cycle Phase 3: cost data collection • Variance at completion (VAC). The variance at completion is the difference between what the project should have cost (BAC) and what it is expected to actually cost (EAC): VAC = BAC – EAC. • For example: CV = BCWP – ACWP = $75000 - $90000 = - $15000 (i.e. a cost overrun of $15000) SV = BCWP – BCWS = $75000 - $50000 = $25000 (I.e. ahead of schedule by $25000) TV = STWP – ATWP = 3 months – 2 months = 1 month (I.e. one month ahead of time schedule) CV ratio = BCWP/ACWP = 75000/90000 = 0.83 SV ratio = BCWP/BCWS = 75000/50000 = 1.5 TV ratio = STWP/ATWP = 3 : 2 = 1.5 • Underperformance is indicated by a ratio less than one unity which confirms in the current example, that cost running above budget. The PCCS operating cycle Phase 3: cost data collection The straight line relationship shown is typical of the early stages of the work package. Most work packages will go on to exhibit the curved shape shown in the next slide. The PCCS operating cycle Phase 3: cost data collection The PCCS operating cycle Phase 3: cost data collection • Multilevel earned value analysis. – Another advantage of EVA is the ability to develop multilevel variance summaries for different levels in the project. In order to do this effectively, the EVA system has to work in conjunction with a CDES (Computerized database estimating systems ). – Using a CDES, the original budget plan is primed with budgeted cost (BC) values. These values remain constant throughout the life cycle, except where official changes are made through the CAC (cost accounting codes) change control system. The ACWP values for each cost center are automatically charged to that cost center by accounting control or through whichever section is responsible for setting invoices and paying salaries. The work scheduled (WS) figures are stored in the project schedule and can be automatically linked to the CAC network for the project. The PCCS operating cycle Phase 3: cost data collection – Linking the CDES, DMS and payment records allows BCWP, BCWS and ACWP to be automatically calculated at different levels through the project, thus allowing the development of a roll-up analysis. The sum total of all the costs and schedule variances on a particular level form the total at the next level for the collective work element. The PCCS operating cycle Phase 3: cost data collection The PCCS operating cycle Phase 4: generation of variances Variance and variation envelope. A variance is any cost or schedule deviation from a specific and predetermined plan. Permitted variances are usually larger in the early stages of a project becoming smaller as the project progresses. • The variance envelope defines the limits of acceptable performance around the mean, beyond which some kind of alarm bells should start to sound. • Analysis of this variance envelope is one of the main applications for the monitoring and control aspects of EVA. The values for CV and SV can be used together to show the cost and schedule performance of any individual WBS element and also for groups of elements using a roll-up analysis. • The variance generation process involves looking at CV and SV in order to assess the performance of individual work packages and groups of work packages. The PCCS operating cycle Phase 4: generation of variances • Variance interpretation. – Cost variance CV = BCWP – ACWP Therefore BCVP > ACWP: work performed has cost less. BCWP < ACWP: work performed has cost more. BCWP = ACWP: work on cost plan. – Schedule variance SV = BCWP – BCWS Therefore BCWP > BCWS: work ahead of program. BCWP < BCWS: work behind program. BCWP = BCWS: work on program. The PCCS operating cycle Phase 4: generation of variances – These values can also be shown as indices. – Cost Variant Index CVI = BCWP/ACWP CVI > 1.0: good; CVI < 1.0: bad; CVI = 1.0: OK. – Schedule Variance Index SVI = BCWP/BCWS SVI > 1.0: good; SVI < 1.0: bad; SVI = 1.0: OK. • There are several different ways of interpreting cost and schedule variance figures, and immediate appearances might not always be a true reflection of the situation. • Example interpretations could be as follows: The PCCS operating cycle Phase 4: generation of variances • • • • • • • • • CVI > 1.0, SVI > 1.0. Excellent: the project is under cost and ahead on program. CVI > 1.0, SVI =1.0. Good: the project is under cost and is on schedule. CVI > 1.0, SVI < 1.0. Good/bad: the project is under cost but behind on program. CVI =1.0, SVI > 1.0. Good: the project is on cost and ahead program. CVI = 1.0, SVI =1.0. Good: this scenario means that the project is on cost and on schedule. CVI = 1.0, SVI < 1.0. Bad: the project is on cost but is behind schedule. CVI < 1.0, SVI > 1.0. Good: the costs are over the projection, but the project is also ahead of program. CVI < 1.0, SVI = 1.0. Poor: the project has a cost overrun and is on program. CVI < 1.0, SVI < 1.0. Very bad. The PCCS operating cycle Phase 4: generation of variances • • The indices can be used as a direct indicator of performance by showing them against axes ranging from zero to unity. This kind of presentation can be useful as it shows easily the effect that different actions are having on the cost and schedule performance of the project. The PCCS operating cycle Phase 4: generation of variances The critical ratio. • The “alarm” system that operates in association with the variance envelope is critical. The alarm trigger often makes use of the critical ratio.: actual progress Critical ratio scheduled progress budget cost actual cost • The critical ratio uses EVA principles in that it includes consideration of both time and cost performance. • The critical ratio is also useful in that the project manager can apply relative weightings to the time and cost elements. F.e., time may be more important than cost on a given project. Multiplying the time element, for example by 0.5, effectively amplifies the importance of the time element relative to cost. Actual progress has to be twice as great for a time value of unity to be obtained. • Critical ratio are often shown as diagrams. The PCCS operating cycle Phase 4: generation of variances Typical zone classification are listed below: • Zone A: Take no action. The lower limit for this zone is established at the outset. • Zone B: Record and monitor. This zone contains more significant negative variations that cannot be ignored. The negative variation may not be regarded as critical but any variations that continue to move downwards may be a cause for concern. • Zone C: Act immediately. Immediate variance analysis and corrective trade-offs are required. • Zone D: Emergency response required. These variances are supercritical. • Zone A1: Observe and note. Activities that fall into this zone could be useful for feedback and for involvement in change notices. • Zone A2: Investigate and correct. This zone contains activities with large positive variances. It should not be possible for an activity to reach this zone so there is clearly a problem. Typical reasons include pessimistic estimating, poor quality control, poor supervision, undetected errors and omissions. The PCCS operating cycle Phase 5: cost reporting • Reporting is the first step towards monitoring, analyzing and ultimately managing the progress of any project. • Good-quality information is the key to good project decision making and therefore good project management. • The quality and nature of the project reporting system will directly influence the quality, appropriateness, and timeliness of the information provided to managers and upon which they will base their decisions. The PCCS operating cycle Phase 5: cost reporting • In general reports should: – be produced on time; – include only relevant information; – allow for all interrelationships between the data contained in them;’ – be honest and accurate; – be issued to everybody who is involved; – highlight particularly important issues; – put forward proposed solutions (where appropriate); – put forward clear responsibilities and time scales for implementation (where appropriate). The PCCS operating cycle Phase 5: cost reporting • When used properly reports can be extremely useful. Timely well-written reports can: – improve the overall understanding and efficiency of the project team; – provide early warning of potential problems; – act as an overall stabilizing mechanism; – contribute to the project audit trail; – provide essential data to act as the basis for management decision making; – assist in progress reviews; – improve coordination of management response. The PCCS operating cycle Phase 5: cost reporting • Basic report types: – Routine reports are issued routinely. These are used primarily to keep team members up to date on the everyday performance of the project. Routine reports tend to be specific: cost reports, schedule progress reports, quality reports, risk reports. Large projects tend to have review meetings. – Development review reports are used where the project team is undergoing any kind of development program or where the project itself is subject to review. This type of report is typical on research and development projects where the precise work content is not known at the outset. – Exception reports are issued primarily to highlight an exception where something has occurred that is out of the ordinary. – Subject specific reports are produced where a specific aspect of the project is causing concern and where detailed monitoring and control is required. – Project variance and analysis report (PVAR) combine the approaches listed above. The PCCS operating cycle Phase 5: cost reporting • PVAR reporting use EVA as the primary analysis tool. – A PVAR report is generated directly from cost data and would normally be assembled each month. – The report shows the variance performance of the project as a whole and then moves down to finer levels of detail according to the WBS breakdown used by the CDES. – The PVAR report itself would typically show: • routine reporting information; • development progress and review information; • the performance of each level of the WBS in terms of: ACWP, BCWP, BCWS, CV, SV, EAC, ETC. • any significant cost or schedule variances; • sources and reasons of such variances; • proposal responses together with individual responsibilities, action plans and time scales. The PCCS operating cycle Phase 5: cost reporting • For each problem cost center, separate PVAR reports are generated showing: – WBS identifiers (project, elements, sub-elements etc.); – CAC identifier and approved budget limits; – current values of ACWP, BCWP, BCWS, CV, SV, BAC, EAC, ETC and VAC figures; – previous month (or other reporting period) corresponding values; – summary of differences between previous month and current month values; – summary of significant differences (improvements and deteriorations); – current EAC, ETC, ECTC, ETTC values. • The PVAR report would probably show the curves given in the next slide. Анализ заработанной стоимости (Earned Value Analysis) The PCCS operating cycle Phase 5: cost reporting • Once the value in terms of performance variables has been established for every task, the only input required to make the system work is the approximation of works completed. Once this has been input, the EVA system can quickly and easily calculate the following parameters: – Earned value is the money that has been earned by doing the work to date. It is equivalent to the budget cost of the work multiplied by the amount of work completed and valued. – Earned value hours are the total budgeted number of hours multiplied by the proportion of total hours actually completed. This shows the proportion of earned value that has already been achieved and gives an indication of the proportion that remains. – Anticipated final hours are the total budgeted number of hours divided by the proportion of total hours actually completed. – Project efficiency is the earned value hours divided by the total hours actually completed. – Project progress is the earned value hours divides by the total budgeted work hours. Основные понятия анализа заработанной стоимости • • • • • • • • • • • • BCWS – Budgeted cost of the works scheduled (planned earned value) - расчетные издержки планового объема работ; ACWP – Actual cost of the works performed – фактические издержки выполненного объема работ; BCWP –Budgeted cost of the works performed (actual earned value) – расчетные издержки выполненного объема работ; STWP - Scheduled time for work performed – расчетное время выполнения работ; ATWP - Actual time for work performed – фактическое время выполнения работ; ECTS – Estimated cost to complete the project – остающиеся расчетные издержки до завершения проекта; ETTS – Estimated time to complete the project – остающееся расчетное время до завершения проекта; BAC – Budget at completion – полная плановая стоимость проекта; EAC – Estimate at completion – оценка фактической стоимости проекта к моменту завершения; VAC – Variance at completion – превышение стоимости проекта; SV - Schedule variance – отклонения от плана; CV – Cost variance – отклонения стоимости. Реальность планирования Часто в начале проекта легкомысленно подходят к оценке продолжительности работ и принимают обязательства, которые потом не могут быть выдержаны. Как слишком завышенные, так и заниженные задания приводят к повышению издержек, а недоверие к реальности планирования приводит к отсутствию дисциплины. Если опыт показывает, что планы нереальны, то им больше не верят и игнорируют. Управление рисками Закон Мэрфи: Если какая-нибудь случается. неприятность может случиться, - она Первый закон Чизхолма: все, что может испортиться – портится. Следствие: Все, что не может испортится, - портится тоже. Второй закон Чизхолма: Когда дела идут хорошо, что-то должно случиться в самом ближайшем будущем. Следствия: 1. Когда дела идут хуже некуда, в самом ближайшем будущем они пойдут еще хуже. 2. Если вам кажется, что ситуация улучшается, значит, вы чегото не заметили. Управление рисками Т Третий закон Чизхолма: Л любую цель люди понимают иначе, чем человек ее указующий С Следствия: 1. Если ясность вашего объяснения исключает ложное толкование, все равно кто-то поймет вас неправильно. 2. Если вы уверены, что ваш поступок встретит всеобщее одобрение, кому-то он не понравится. Project Risk Management Introduction • Projects tend to be complex and one-off. They may operate within an environment that is characterized by uncertainty. • The project manager has to make decisions under conditions where risk is an everyday factor. • The project manager has to be able to analyze the project and its environment, and identify the risks that are present. • The project manager has to be able to transfer or reduce unacceptable risks and then set up monitoring and control systems so that residual risk can be managed effectively. Background to risk The concept of risk • • • • Risk and opportunity go hand in hand. Everybody is on the lookout for a good opportunity. Opportunities exist within an uncertain world and are therefore subject to uncertainty and risk. In order to succeed, companies have to take risks. The relevant risks have to be effectively managed if opportunities are to be exploited. Risk and risk management should not be seen static. Risk is therefore both a good thing and a bad thing. It is a driving force behind innovation and enterprise, but it also a threat if not properly evaluated and managed. Background to risk The concept of risk • In general terms, the decision maker acting under conditions of risk would be most concerned with the following questions: – – – – What can go wrong with the project? What possible outcomes do we face as a result of these risks? Where do these risks and consequent outcomes originate? Do we have any control over these risks and if so are we using it? – Are the risks and consequent outcomes related to any extent? – What is the degree of exposure of the organization to these risks? – How sensitive is the organization to each degree of exposure? Background to risk The concept of risk – Do this risks affect the achievement of the overall strategic objectives of the organization? – What response options do we have? – What contingencies or emergency responses are in place? – Can we match the worst case scenario? – If not which scenario riches the limit of our response abilities? – What is the potential reward associated with each risk? – Are we prepared to accept a risk and corresponding outcome that is beyond our limits to absorb? Виды рисков Суммарный риск проекта содержит в общем случае четыре больших группы рисков: - технические риски; - экономические риски; - политические риски; - социокультурные риски. Наиболее частым источником рисков являются стыки. Успешное наведение мостиков в местах стыков различных частей системы является одной из важнейших задач проекта. Технические риски Источниками технических рисков являются инженерные ошибки, дефекты поставки сырья и материалов, ошибке при изготовлении, монтаже и сдаче в эксплуатацию. Примером инженерной ошибки может быть неудовлетворительное проектирование, из-за которого не достигается запланированная производительность установки или не соблюдены действующие в стране потребителя законы, нормы и правила. Под дефектами поставки сырья и материалов понимают ситуации, когда не соответствует требованиям проекта их качество или количество, а также, если они поставляются с опозданием. Технические риски Риски при изготовлении, монтаже и сдаче в эксплуатацию связаны, главным образом, с квалификацией персонала и поэтому их особо трудно оценить. Риски могут также возникнуть и потому, что в других климатических или географических условиях известные приборы, установки или технологии реагируют неожиданным образом. Нередко имеет место и ситуация, когда в месте монтажа своевременно не подготовлена площадка или подъездные пути, отсутствуют необходимое сырье, материалы или их качество и количество не соответствует нуждам проекта и т.д Одним из важнейших факторов риска, особенно в условиях Сибири, является климат. Экономические риски • В группу экономических рисков входят: 1. Финансовые риски. 2. Риски взаимодействия с клиентами. 3. Риски взаимодействия с партнерами по кооперации и поставщиками. 4. Риски в управлении проектом. 5. Информационные риски. 6. Риски, связанные с отсутствием квалифицированной рабочей силы. Особенно важны риски, связанные с финансированием проекта – платит заказчик согласованные суммы аккуратно или нет, темп инфляции, курс валюты и др. Экономические риски Риски взаимодействия с клиентами, партнерами по кооперации и поставщиками связаны обычно с пробелами в договорах или плохо разграниченных позициях договоров. Если договор выполняется за рубежом, то возникает дополнительный риск, связанный с проблемой нахождения квалифицированного руководства проекта на весь период выполнения работ. Может возникнуть и целый пакет проблем, связанных с недостаточной коммуникацией и информацией, например, языковые проблемы, отсутствие или низкое качество связи между местом работы и материнской организацией. В отдаленных районах и за рубежом могут возникнуть дополнительные проблемы, связанные с отсутствием квалифицированной рабочей силы. Высокие риски могут быть также обусловлены разным подходом к работе и разной трудовой моралью, связанные с иными установками в регионе или стране с другой культурой. Экономические риски Проекты с традиционно высокими рисками (например, проекты внедрения электронного документооборота или проекты реконструкции) при твердо установленной стоимости могут быть связаны с большими опасностями не только для исполнителя, но и для заказчика. Исполнитель будет всегда стремиться выполнить проект без убытков, даже за счет снижения качества работ. Поэтому в таких случаях рекомендуется браться за проекты с твердой стоимостью (также как и поручать их) только после основательного анализа рисков и четкого согласования условий. Другая разумная альтернатива заключается в том, чтобы твердую стоимость устанавливать только для частей проекта с обозримыми рисками, а остальную часть принимать по фактическим затратам, что позволяет уменьшить финансовую неопределенность проекта Политические риски Политические риски могут быть связаны с: запретом или ограничениями при перевозке различных грузов; требованиями по участию в выполнении работ местных предприятий; дополнительными налогами или особыми обязательствами; влиянием местных групп с различными интересами, а также ограничениями на трансфер капитала; принуждением к использованию местного персонала; односторонним толкованием договора; осложнениями/разрушениями, связанными с вооруженными конфликтами; национализацией собственности. Социокультурные риски В зарубежных проектах особое значение приобретает разнообразие культурных и социальных условий. Сюда относятся, прежде всего, такие институциональные факторы, как семья, клановость, религия и др. Кроме того, следует учитывать специфические представления о ценностях, которые могут, например выражаться в сопротивлении населения новшествам, существовании черных рынков, семейственности, ненависти к иностранцам, особых традициях и т.д. Types of risk Generic risk headings • Broad headings are: – Strategic risk. It includes a range of variables such as the market, corporate governance and stakeholders. – Operational risk. It includes the process itself, the asset base, the people within the project team and the legal controls within which the organization operates. – Financial risk. It includes market, credit, capital structure and reporting risk. – Knowledge risk. It includes IT hardware and software, information management , knowledge management, and planning. – Catastrophic risk. It includes risk that cannot be predicted effectively and therefore cannot be quantified accurately. • Within these broad headings for risk types, there are several specific subdivisions that can occur. Market risk (business risk or dynamic risk) • • Market risk is measured by changes and variations in the general marketplace. It is unavoidable, since it relates to factors that are outside the control of the decision maker and could result in positive or negative impacts. Market risk therefore provides the organization with the potential for both profit and loss on trading. Obvious examples would include: – – – – – • • share floatation; competitor activities; investment in research and development; release of new products; general economic activity. Market business risk (MBR) arises from the company trading with its assets. It is a risk to the company as a whole, and it therefore distributed among the shareholders, creditors, employees and all other stakeholders. Market financial risk (MFR) arises from the gearing ratio, which is the measure of the financing of the organization. MFR is the risk of the annual dividend falling to zero, so that equity holders make no return on their shareholdings. Static risk (specific risk or insurable risk) • Static risk considers losses only. • It looks at the potential losses that could occur and seeks to implement safeguards and protection in order to minimize the extent of the loss. • The obvious examples would include: – – – – – fire insurance; third party and public liability insurance; professional indemnity insurance; personnel insurance; other optional forms of insurance. • The organization can reduce the effects of specific risks by insuring against them (where relevant) and by diversifying. By expanding the range of new areas within an organization, the organization spreads the specific risk and makes the system more resilient against market-risk shocks, such as a sudden change in statute or a change in government fiscal policy. Static risk (specific risk or insurable risk) • • • Static risk considers losses only. It looks at the potential losses that could occur and seeks to implement safeguards and protection in order to minimize the extent of the loss. The obvious examples would include: – – – – – • fire insurance; third party and public liability insurance; professional indemnity insurance; personnel insurance; other optional forms of insurance. The organization can reduce the effects of specific risks by insuring against them (where relevant) and by diversifying. By expanding the range of new areas within an organization, the organization spreads the specific risk and makes the system more resilient against market-risk shocks, such as a sudden change in statute or a change in government fiscal policy. Predictable and unpredictable risks • Predictable risks are “known unknown” risks, such as changes in interest rates during times of fluctuation in the economy. They can be predicted with some accuracy although not with certainty. • Unpredictable risks are the “unknown unknowns”. This cannot be predicted with any accuracy. F.e., a dynamic internal unpredictable risk could be a project status change. Выявление рисков • Основные методы: 1. Определение риска на основе структурного плана проекта. 2. Анализ отказов. 3. Контрольные листы. • Последовательность действий при определении рисков на основе структурного плана проекта: – выявление рабочих пакетов, связанных с большими рисками, – определение возможных трудностей и количественная оценка рисков, – выявление возможных причин трудностей, уменьшение или исключение проблем с наибольшей степенью риска. Выявление рисков • Для определения рабочих пакетов, связанных с наибольшими рисками все работы включаются в список, и каждая из них исследуется с помощью следующих вопросов: – могут ли возникнуть трудности в содержательной области? (содержательный риск); – могут ли возникнуть трудности с соблюдением сроков? (временной риск); – имеется ли сильное ограничение по финансам? (финансовый риск). • Для каждого рабочего пакета записываются все мыслимые трудности, указывается вероятность их возникновения и определяются затраты, которые могут понадобиться на их устранение. • Этот подход к анализу рисков может быть применен для всех типов проектов и может быть начат в любых их фазах. Выявление рисков Выявление рисков на основе анализа отказов базируется на том, что проблемы часто возникают, когда появляются отклонения технологических параметров (количества, давления, температур, времени обслуживания клиентов и др.). Поэтому ставится цель зарегистрировать все мыслимые отклонения от нормальной эксплуатации и их проанализировать. Если речь идет об установке, то исходя из схемы установки, по каждой из входящих в нее составных частей, записываются все возможные отклонения процесса от нормы, определяются их причины и последствия. При методе контрольных листов используются детальные контрольные списки (вопросники), составленные на основе опыта (своего или чужого) выполнения прошлых проектов. Анализ риска проекта • Анализ риска проекта должен включать: – источники рисков; – факторы рисков; – оценку рисков. Значимость риска зависит от: - последствий его проявления, - вероятности возникновения, - эффективности мер противодействия. Background to risk The concept of risk • • Risk in the context of project management is a measure of the probability and consequence of not achieving specific project goal. It depends both on the likelihood (probability) of an event occurring and the consequences (impact) of that event should it occur. Risk is a function of the probability of an event occurring and the consequences of the event if it does happen: Risk = f (event, uncertainty, consequences). • Risk is also a function of the level of hazard represented by an event and the degree of the safeguard that is put in place to counter it: Risk = ( event, hazard, safeguard). Risk conditions and decision making • Risk is intrinsically linked to decision making. • There are generally three main conditions under witch decisions can be made: – conditions of certainty; – conditions of risk; – conditions of uncertainty. • Conditions of certainty apply where the outcome is known. • Conditions of risk apply where is a reasonable probability that an event will occur and where some kind of assessment can be made. These are the “known unknown” events. Most risk management and decision making take place under conditions of risk. • Conditions of uncertainty apply where is not possible to identify any known events. It is not possible to predict outcomes with any accuracy. Decision making under conditions of certainty • Decision maker knows with 100% accuracy what the outcome will be. • Conditions of certainty can be represented using a pay-off matrix, where profit for each strategy and state of nature are shown. Strategy Possible stage of nature N1 = up N2 = even N3 = down S1 = A $100 000 000 $80 000 000 $60 000 000 S2 = B $150 000 000 $100 000 000 $80 000 000 S3 = C $200 000 000 $160 000 000 - $100 000 000 Decision making under conditions of risk • In most practical situations, there is no single dominant strategy for all eventualities. In general terms: Higher profits = higher potential risks Higher profits = higher potential losses. Strategy Possible stage of nature N1 = up N2 = even N3 = down Probability = 25% Probability = 25% Probability = 50% S1 = A $100 000 000 $80 000 000 $60 000 000 S2 = B $150 000 000 $100 000 000 $80 000 000 S3 = C $200 000 000 $160 000 000 - $100 000 000 The expected payoff for each strategy now is the sum of the payoffs for each state of nature multiplied by the probability of that state occurring: S1 = (100m x 0,25) + (80m x 0,25) + (60m x 0,5) = $75m S2 = $102,5m; S3 = $40m. Decision making under conditions of uncertainty Uncertainty criteria • Under conditions of uncertainty, it is not possible to predict what state of nature will apply. One of several uncertainty criteria may then apply – Hurwicz criterion (maximax criterion). – Wald criterion (maximin criterion). – Savage criterion (minimax criterion). – Laplace criterion. Rules for decision making under conditions of certainty, risk and uncertainty • Any of the four uncertainty strategies can be adopted, depending on: – – – • how much money we can afford to lose; the level of risk that we are willing to take; what level of risk outcome that we can absorb. In terms of general risk taking: – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – Don’t risk a lot for a little unless it is really worth it; Always analyze risks very carefully; Make sure that all risks have been identified; Make sure that all possible implications have been identified; Consider risk in terms of exposure and sensitivity; Plan for risk in as much details as possible; Always include an contingency plan; Don’t accept risks for reasons of principle; Don’t accept risks to avoid losing face; Never risk more than you can afford to lose (unless you have to); Consider odds and intuition; Allow for the effects of bias; Allow for the effects of groupthink; Consider controllable and uncontrollable aspects separately; Eradicate unknown factors as far as possible. Rules for decision making under conditions of certainty, risk and uncertainty • In terms of hazard and safeguard: – – – – – – • Maintain a low center of gravity; Reduce the risk profile where possible; Try to take risks in non-critical areas; Consider defenses in relation to potential hits; Maintain safeguards within reasonable limits; If in doubt, ask the boss. In terms of group development: – – – – – Allow for groupthink; Beware unfounded delusions; Remember that groups make more risky decisions than individuals; Don’t confuse risk taking with boldness; It is something prudent to be wary. Rules for decision making under conditions of certainty, risk and uncertainty • In more philosophical terms: – – – – – You can’t to avoid risk so accept it; Be prepared to take risks or you won’t to be able to exploit opportunities; Engineer risk to keep it within acceptable limits; Use vision and think in expansive terms. Don’t allow risk to put you off; Try new things because if you don’t you may become entrenched in the known and become fearful of the unknown; – Use risk to make money. Источники рисков - по персоналу: - по руководителю проекта, - по работникам проекта, - по работникам предприятия, которых затрагивают проектные решения, - по советам предприятия, - по лицам ответственным за безопасность, защиту информации, охрану окружающей среды. Факторы риска - пожелания о внесении изменений в проект, - несоблюдение бюджета проекта, - проблемы с внешними ресурсами, - появление новой техники, - стремление к совершенству, - проблемы с персоналом, - ошибки планирования, - ошибки по ходу выполнения проекта, - технические проблемы, - влияние окружающей среды, - соблюдение сроков выполнения проекта и его этапов, - пригодность результатов, - дополнительные требования. Оценка рисков Значимость риска зависит от последствий его проявления, вероятности его возникновения и эффективности мер противодействия этому риску. Часто эти три характеристики не удается выразить в цифрах. В этих случаях их ранжируют. Для наиболее вероятных и опасных рисков следует продумать контрмероприятия и учесть их при планировании проекта. Поскольку по ходу проекта возникают новые риски, да и ранее выявленные могут оцениваться по новому, то в течение проекта необходимо периодически возвращаться к анализу рисков и производить их переоценку. Оценка риска проекта Факторы риска Последствия Вероятность возникновения Эффектив ность мер противодействия Значение Ранг Нарушение сроков поставки поставщиками 2 1 5 10 1 Совместимость с окружающей средой 6 3 1 18 3 Совместимость компонентов 4 6 4 96 6 Нехватка персонала 5 2 7 70 5 Пожелания о внесении изменений 3 4 2 24 4 Конфликты в проектных группах 7 7 6 294 7 Проблемы получения разрешений 1 5 3 15 2 Оценка политического риска При зарубежных проектах руководству проекта следует обязательно разобраться с политическими рисками в соответствующей стране и попытаться оценить их возможное развитие в период выполнения проекта. Подходящим методом для этого является техника анализа ценности. Для оценки политического риска в какой-либо стране может быть использован индекс BERI (Business-Environment-Index), который трижды в год составляется 100 экспертами методом Дельфи на основе следующих критериев: · политическая стабильность, · установки по отношению к иностранным инвестициям и прибыли, · степень государственного участия в экономике, · уровень инфляции, · платежный баланс, · бюрократизм, Оценка политического риска · · · • экономический рост, соблюдение договоров, уровень зарплаты и производительность труда, конвертируемость валюты, · наличие экспертов и сферы услуг, · связь и транспорт, · местный менеджмент и партнеры, · возможность получения краткосрочных кредитов, долгосрочных кредитов, наличие собственного капитала. Суммарный индекс может меняться в пределах от нуля до ста. Если в результате оценки получается менее 40 пунктов, то сотрудничество с этой страной, даже при весьма привлекательных проектах, рекомендовано быть не может. The concept of risk management Risk classification Risk types Specific risk (insurable risk) Potential losses: Fire Flood Breakdown Theft Market risk (business risk) Potential gains and losses: Share value Sales Profitability Acquisitions Risk source and scope Environmental risk Specific market or sector risk Specific company risk Specific company project risk Risk impact High impact risk Medium impact risk Low impact risk Example of risk classification system Type Extent Specific Environment Sector Company Project Market Environment Sector Company Project Impact Low Medium Severe Low Medium Severe Low Medium Severe Low Medium Severe Low Medium Severe Low Medium Severe Low Medium Severe Low Medium Severe Example Change in restrictive legislation Establishment of regulatory authority for sector Bankruptcy Extensive fire damage Extreme change in economy Extreme changes in industrial activity Extreme changes in share price Change of project aim Уменьшение рисков Часть рисков может быть распределена на другие организации. Фиксация распределения рисков осуществляется в договорах с членами консорциума, договорах с поставщиками, страховщиками, банками и другими носителями рисков. По рискам, остающимся у подрядчика, должны быть приняты соответствующие технические и предпринимательские меры противодействия. Результаты анализа рисков представляются руководству предприятия для принятия решения о том, браться за проект или нет. Risk handling Approaches to handling risk • The bunker approach. – Decision makers try to allow for every possible risk and price accordingly. They assume the the worst-case scenario and try to recover every possible result. – The obvious end result is a very expensive initial estimate for the project. – This approach is often used for high-quality projects or those where the consequences of failure are large. – Overprovision can itself constitute a risk. In trying to analyze and allow every possible scenario, the product itself may become so expensive that it is no longer viable. Risk handling Approaches to handling risk • The ostrich approach. – It assumes that everything will be all right. (AGAP – All Goes According Plan) – Sometimes the people get away with it; at other times the result is a catastrophe. • The ”gut reaction” approach. – Some experienced decision makers use their intuition. – Gut reaction uses a combination of knowledge, experience, extrapolation and subjective assessment. – This approach is itself risky. It is not normally recommended and tends to be used where there is no other form of assessment. • The aggressive approach. – It assumes that uncontrollable risks can be brought under control by pure aggression and determination. Risk handling Risk assessment and control • • • • There are two essential components in any project risk management strategy. There are project risk assessment and project risk control. A risk management strategy should be developed in detail for a project before the project actually starts, the strategy being implemented as early as possible in the life cycle of the project. Project risk assessment is the process of evaluating and describing the risk in some way that allows objective or subjective evaluation and appraisal. Project risk control is the operational process for measuring actual and planned risk and monitoring the variance between the two as the basis for corrective action. Risk handling Risk assessment and control • There are three components of risk control. There are risk analysis, risk handling, and risk feedback. • Risk analysis involves the determination of the probability of individual risky events occurring, and also of establishing some measure of the potential consequences of each event occurring. • Risk handling is the process of dealing with risks in order to reduce the likelihood of individual events occurring. • Risk feedback is the process where the results of occurred risks are analyzed and any results and items for use in future strategies are fed back into the system. Risk handling Risk assessment and control Project risk management Project risk assessment Project risk control Identify risk Measure and control risk Analyze risk Respond to risk Classify and prioritize risk Propose risk response Analyze residual risk Mitigate residual risk Establish contingencies The concept of risk management Analysis Work breakdown structure Risk identification Risk checklist Internal Risk classification Controllable Probability of occurrence Risk analysis Impact of occurrence Risk-averse Management Risk-neutral Risk attitude Risk-seeking Risk response Risk management strategy Risk holder The concept of risk management Risk analysis – risk map • • The process of risk mapping is sometimes referred to as risk profiling or even risk footprinting. It is basically a process of showing the relationship between risk probability and impact for a range of given risks as a function of time. A basic risk map has four quadrants, although it may be expanded to more sectors: – – – – • Quadrant Quadrant Quadrant Quadrant 1: Red zone (high impact and high probability). 2: Upper yellow zone (high impact and low probability). 3: Lower yellow zone (low impact and high probability. 4: Green zone (low probability and low impact). The risk map is dynamic. It shows the migration of certain risks over a period of time. The concept of risk management Risk analysis – risk map High impact High impact Low probability High probability C Low impact Low impact Low probability High probability A A B Probability The concept of risk management Risk analysis – target risk map Production capacity Major plant failure Labor problems Competitor innovation Product obsolescence Day-to-day errors Minor equipment failure Probability The concept of risk management Risk analysis – risk map with variability limits A A B C C D Probability Уменьшение рисков Риски проекта Принятые подрядчиком риски Риски, возложенные на заказчика Риски проекта, адресованные контрагентам и поставщикам Риски, переданные страховщикам и подобным носителям рисков Риски проекта оставшиеся у подрядчика Распределение общего риска между участниками проекта The concept of risk management Risk analysis – risk response • Risk response basically centers on risk distribution. • The distribution of risk will depend on a number of n0ncontractual considerations: – – – – Is the outcome of the project worth the risk? Who has the greatest risk control? Who has the greatest risk liability? What incentive does each party have? • Most forms of contract require a more or less collaborative approach to the equitable sharing of risk. • Risk response include: – – – – risk retention; risk reduction; risk transfer; risk avoidance. The concept of risk management Risk analysis – risk response • • • • • • Ignoring the risk is obviously itself a high-risk strategy. Informed risk retention is another consideration. This is most suited to risks that are characterized by small and repetitive losses. Risk may be reduced by a number of means. It may be possible to engineer risk out of the equation. In edition, risk may be reduced by training and development, or by redefining the aims and objectives of the project. Risk transfer involves transferring the risk to others. Risk transfer through insurance transfers the risk to the insurance company in return for a premium. Risk can also be transferred through damages clauses within contracts (or through negotiations). Not all risks can be transferred, and there may be some risks where it is not economical to do so. Risk avoidance means removing the risk in all forms from the project. Risk may sometimes be avoided or reduced by seeking additional decision-relevant information. The concept of risk management Common insurance and transfer clauses Insurance clauses Transfer clauses Client •Fire insurance •Flood insurance •Perils (e.g. civil commotion) •Damages •Determination Contractor •All-risks policy •Third-party insurance (damage to persons) •Third-party insurance (damage to property) •Undermining (where appropriate) •Escape (where appropriate) •Retention •Damages •Determination •Performance bond •Warranty •Collateral warranty The concept of risk management Risk analysis – risk control, policy and reporting • • • • • Risk control is the process of using the information that has been learned on a project to assist in the later development of the project. The risk identification and analysis systems may be incorrect or items may have missed. It is very important that all assumptions and evaluation processes are recorded and then measured in some way in order to see whether or not they are working correctly. In addition, the probability and impact of identified risks may change over time. It is important that identified risks are constantly monitored and reviewed. Experience with risk and risk management is often documented into a risk handbook. There must be regular reporting on red-quadrant risks. The concept of risk management Risk analysis – risk control, policy and reporting • Risk report should be produced to a timetable and be controlled by an overall strategy. • The level and frequency of reporting will depend on the significance of the risk: – The CEO would usually receive frequent progress reports, including identified risk drivers and detailed risk maps. – The Board would receive copies of these, and also intermediate sixmonthly reports. – For periods less than six months, progress would be summarized by executive managers and circulated within the various project teams. – The CEO and senior managers receive informal communication on progress on all levels. The concept of risk management Risk analysis – risk control, policy and reporting • Risk policy is a statement of the policy of the organization in terms of risk and risk management. • Over and above the identification of risk holders and risk strategies for “red quadrant” risks the risk policy establishes a number of elements: – – – – – Overall aims and objectives. Accountability for individual managers. Formalized reporting channels. Risk tolerances. Authorization. • Any risk policy should initially develop individual targets for individual sections within the organization. Once this has been completed, the policy is developed and worked up as a strategic document.