Lecture № 1
реклама

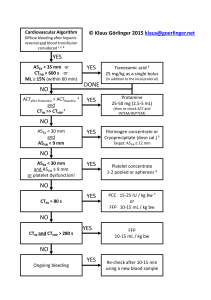
Lecture № 1 The subject of the problem of topographic anatomy and operative surgery primary treatment of wounds Closure of skin defects • Topographic anatomy - the study of the morphological structure of the different regions of the human body. • TOPOS - the place and the GRAPH - I write. Hence - topographic, ie Regional (regional) anatomy. 1) Layered topography - ie successive layers outcrop area, from the skin. 2) Golotopiya - position of authority in relation to the human body. The liver, for example, is golotopicheski at right hypochondrium and epigastric abdominal cavity and the heart - in the anterior mediastinum and thoracic cavity, etc. 3) syntopy - the ratio of the body to the surrounding organs and tissues. Thus, behind the stomach adherent pancreas, bottom poperechnoobodochnaya intestine, stomach in front of the front abdominal wall, etc. Relationships are described and with n t o p u and body. 4) Skeletopiya body, its relation to the level of the skeleton. Thus, renal pedicle skeletotopicheski located at the level II of the lumbar vertebrae, pylorus - XII breast etc. 5) A typical anatomy, design a school professor. V.N.Shevkunenko studying the variants of the structure of organs and their extreme morphological types in connection with a wide variety of shapes and positions. • 6) Age anatomy - the process of identifying age differences in the location of bodies. 7) Xirurgicheskaya studying anatomy and morphology of the body surrounding anatomical structures in pathological conditions. Method for studying topographic anatomy • Dissection - allocation body, followed by a study. Method cuts Pirogov ("Pirogov slices") to the frozen corpse. The method of "ice sculpture" Pirogov is the design on the frozen corpse of a separate body, by removing all excess tissue using chisel and hammer. Method injections or cordials vessels. SUBJECT of Surgery • Operative Surgery - is the study of surgical operations, addressed the development and study of techniques and good practice surgery. In surgery distinguish two main points: on-line access and operational techniques. • 0perativnym access is the part of the operation, the surgeon ensures outcrop body. The operative technique is called the main part of the operation on the organ. ANESTEZIYA • 1) local anesthesia, 2) nerve block, 3) spinal anesthesia, 4) epidural anesthesia. Surgical instruments: Divided into 5 groups • to disconnect the tissues - scalpels, knives, scissors, saws, chisels, osteotomes, pliers, etc. • to stop the bleeding - hemostat? Kocher, Billroth, Halstead, Mikulic, etc. and ligature needles Cooper and Deschamps. • fixation tools (enhance and support)? tweezers anatomical, surgical, web-footed, blunt and sharp hooks, probes, and large extensions (mirrors), bone fixation forceps. • for tissue - needle holders with sharps needles, instruments for bone joint. • special tools used for ophthalmology, ENT, neurosurgery, cardiology, pulmonology, gynecology and urology. Classification of transactions • radical • palliative By due date Emergency urgent routine healing diagnostic PRIMARY TREATMENT OF WOUNDS • I) wide incision wounds 2) deprived of food and excision of contaminated sites 3) stop the bleeding, 4) removal of free-lying foreign bodies and bone fragments devoid of periosteum, 5) wide drainage of the wound, 6) immobilization of the affected limb. Types of surgical sutures • Primary - Where the operation menee than 6-12 hours after the injury, and if it was possible to excise the wound; Initially delayed - in the case of late avivement 24 hours after the injury - the wound is recommended to flash, but do not leave seams tied, sutures tied in 4-5 days if there are no signs of inflammation in the wound; Secondary - after days, the wound is festering like after treatment stitches. Distinguish 5 types of plastic surgery on the skin • Plastic local tissues, plastic skin graft to pedicle, Free transplantation of skin grafts. the use of cultured allofibroblastov. temporary closure of a biological defect. Виды кожной пластики местными тканями. I и II— по Ю. К. Шимановскому; III — по А. А. Лимбергу; IV — индийский метод; V — итальянский метод (вариант метода). Способы выкраивания кожного стебля по В. П. Филатову. Пластика мигрирующим стеблем по В. П. Филатову Разновидности кожной пластики итальянским методом Взятие расщепленного лоскута кожи Некоторые виды пластики местными тканями 1 — применение послабляющих разрезов; 2 — перемещение прямоугольных лоскутов; 3 — пластика встречными треугольниками Этапы создания стебля по Л. Р. Балону. THANK YOU FOR YOUR ATTENTION