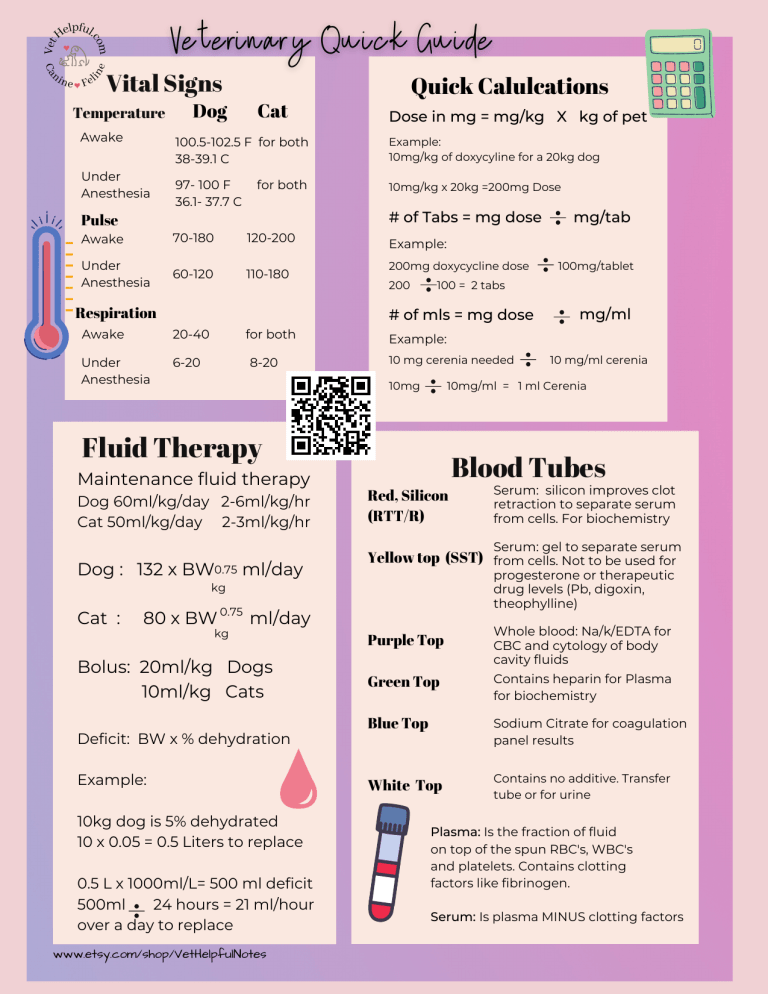
Vital Signs Temperature Awake Under Anesthesia Dog Cat Quick Calulcations Dose in mg = mg/kg X kg of pet 100.5-102.5 F for both 38-39.1 C Example: 10mg/kg of doxycyline for a 20kg dog 97- 100 F 36.1- 37.7 C 10mg/kg x 20kg =200mg Dose for both # of Tabs = mg dose Pulse Awake 70-180 120-200 Under Anesthesia 60-120 110-180 Respiration Example: 200mg doxycycline dose 200 20-40 Under Anesthesia 6-20 for both 8-20 10 mg cerenia needed 10 mg/ml cerenia 10mg/ml = 1 ml Cerenia Fluid Therapy Dog 60ml/kg/day 2-6ml/kg/hr Cat 50ml/kg/day 2-3ml/kg/hr mg/ml Example: 10mg Maintenance fluid therapy 100mg/tablet 100 = 2 tabs # of mls = mg dose Awake mg/tab Red, Silicon (RTT/R) Blood Tubes Serum: silicon improves clot retraction to separate serum from cells. For biochemistry Serum: gel to separate serum Dog : 132 x BW0.75 ml/day Yellow top (SST) from cells. Not to be used for progesterone or therapeutic drug levels (Pb, digoxin, theophylline) kg Cat : 80 x BW 0.75 ml/day kg Bolus: 20ml/kg Dogs 10ml/kg Cats Deficit: BW x % dehydration Example: 10kg dog is 5% dehydrated 10 x 0.05 = 0.5 Liters to replace 0.5 L x 1000ml/L= 500 ml deficit 500ml 24 hours = 21 ml/hour over a day to replace www.etsy.com/shop/VetHelpfulNotes Purple Top Green Top Whole blood: Na/k/EDTA for CBC and cytology of body cavity fluids Contains heparin for Plasma for biochemistry Blue Top Sodium Citrate for coagulation panel results White Top Contains no additive. Transfer tube or for urine Plasma: Is the fraction of fluid on top of the spun RBC's, WBC's and platelets. Contains clotting factors like fibrinogen. Serum: Is plasma MINUS clotting factors IRIS Staging Stage 1 Early Stage 2 Mild Stage 3 Moderate Stage 4 Severe Dogs Creat <1.4 SDMA <18 Cats Creat <1.6 SDMA <18 Creat 1.4-2.8 SDMA 18-35 Creat 1.6-2.8 SDMA 18-25 Creat 2.9-5 SDMA 36-54 Creat 2.9-5 SDMA 26-38 Creat >5.0 SDMA >54 Creat >5.0 SDMA >38 Ideal BP is under 140. Hypertensive: >180 UPC dogs: ideal under 0.2, over 0.5 is high UPC cats: ideal under 0.2 over 0.4 is high Elevated BP and/or UPC negatively impact survival CPCR QUICK GUIDE Most common arrest rhythm in people is V fib, so you shock them. Pulseless electrical activity or asystole is the most common arrest rhythm in pets (so defibrillation not commonly used). Starting chest compressions quickly and using high quality chest compressions to achieve perfusion (allow for full chest recoil). This influenced outcome the most in studies. PEARLS Low dose epinephrine is now recommended over higher doses of epinephrine Shortcut: Epinephrine (1mg/ml) 0.1ml per 10kg Naloxone (0.4mg/ml) 1ml per 10kg Atropine (0.54mg/ml) 1ml per 10 kg Flumazenil (0.1mg/ml) 1 ml per 10 kg Any opioid should be reversed w/ naloxone; consider flumazenil, antisedan If giving intratracheal route: red rubber to the carina, dilute in 5-6 ml sterile saline, double the dose and give 2 good breaths Recommend 2 minute cycles of chest compressions and breathing. Use epinephrine q 3-5 minutes (every other cycle) Best practice to not wet EKG leads in CPR with alcohol in case you need to defibrillate you won't cause a fire. Metabolic Disorders : pH and Bicarb move in the same direction Metabolic Acidosis: The most Metabolic Acidosis frequent pH disorder pH is Causes: DKA, uremia, lactic acidosis (ex: hypotension), Ethylene Glycol poisoning, etc Bicarb is Metabolic Alkalosis pH is Bicarb is Metabolic Alkalosis: Causes: Vomiting up acid, sequestration of Cl from stomach torsion, furosemide ,mineralocorticoid Resp Disorders: pH and Bicarb move in opposing directions Respiratory Acidosis pH is Bicarb is Respiratory Alkalosis pH is Bicarb is www.etsy.com/shop/VetHelpfulNotes Respiratory acidosis : Causes: Hypoventilation caused by airway obstruction, Breathing center depression (drugs), restriction of breathing pneumothorax, effusion, diaphragmatic hernia, etc. Respiratory alkalosis : The least frequent pH disorder Causes: hyperventilation due to hypoxemia, pain, pulmonary edema, pneumonia, embolism etc. Blood Gas Normals Canine pH P02 pC02 HC03 BE Lactate i Ca Venous 7.35-7.45 30-42 40-50 20-24 -4-4 <2-2.5 1.8-1.37 Feline pH P02 pC02 HC03 BE Lactate iCa Venous 7.3-+/- 0.08 38.6-/- 11 41.8 +/-9 19.4 +/k4 -5.7 +/- 5 <2-2.8 1.07-1.47





![ISSN 1561-6274. Нефрология. 2009. Том 13. №3. © Ì.Ì.Âîëêîâ, 2009 ÓÄÊ 616.61-036.12-008.9]:546.41+546.18](http://s1.studylib.ru/store/data/002088276_1-4bc2ed86dc4c87a6d852f5029de422b0-300x300.png)

