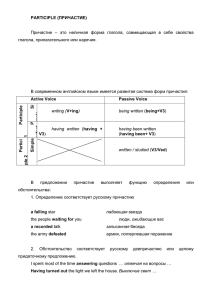
Денежные реформы в истории современной России 02 Денежные реформы В широком смысле – переход от одной денежной системы к другой. В узком смысле – частичные изменения денежной системы. Осуществляются с целью упорядочивания и укрепления денежной системы, сдерживания инфляции, стабилизации экономики в целом. Виды денежных реформ 1 Переход от одного типа денежной системы к другому Например, переход к неразменным бумажно- 2 Или неразменных денежных знаков разменными. кредитным деньгам. 3 Изменения в системе эмиссии денег Замена обесцененной монеты полноценной 4 Стабилизация валюты или частичные меры по упорядочиванию денежного обращения Виды денежных реформ 5 Образование новой денежной системы В связи с государственным переустройством. 05 Денежные реформы могут проводиться самыми разными методами, дополняясь реформами налоговой системы, рынка ценных бумаг, цен и тарифов, валютным регулированием. Классические методы Д Дефляция т.е. сокращение денежной массы путем изъятия из обращения излишних бумажных денег. Д Деноминация Изменение нарицательной стоимости денег с их обменом по определенному курсу на новые, более крупные единицы. Нуллификация 01 02 03 04 Н Ликвидация старых обесценившихся денег и выпуск новых в меньшем количестве, c более высокой покупательской силой Девальвация Уменьшение содержания золота или серебра в денежной единице. Д Классические методы Р Ревальвация Процесс, обратный девальвации. 05 • Замена старых советских рублей новыми банкнотами в 1993-1994 г. В истории современной России • Деноминация рубля в 1998 г. • Дефолт и девальвация рубля во второй половине 1998 г. 09 Заключение Реформы 1998 г. были последними значительными реформами в истории современной России. После них значительных изменений не было. С тех пор денежная система стала стабильной, неизменной. Спасибо! Презентация студента РЭУ им. Плеханова, Беспрозванных Сергея группы 15.06Д-Э01.20Б The economy of France Important features of the French method of initial capital accumulation were: Initial accumulation in France • the extraordinarily large role of the public debt system • relative weakness of the domestic market Feudalism in France 1 3 The isolation 2 Domination of peasant land ownership The isolation of the feudal class from agriculture. Domination in the village of small peasant land ownership, the natural character of which determined the weak development of commoditymoney relations and the narrowness of the domestic market. (tithing).. Strong political positions of feudal lords Special role of state taxes The extremely strong political positions of feudal lords in the state held back the process of decaying feudalism and forming capitalist relations. 4 Special role of state taxes (capitulation - poll lodge, talia - income tax, twenty - 1/20 harvest from communal land) in a kind of centralization of feudal rent. Feudalism in France 5 Government loans at high interest rates Issue of government loans at high interest rates. As a result, usury became more profitable than investing in the development of in-house production. 7 Weak development of private investment in industry The weak development of private investment in industry has led to the royal government's wellknown patronage of crafts and factories. 6 Disenfranchisement of all non-courtiers The complete disenfranchisement of all noncourtiers had a heavy impact on the legal situation of the bourgeoisie. As a result, the process of the development of capitalism in France led to a known "snug" part of the French bourgeoisie. Types of manufactures V State royal manufactories Created and held at the expense of the state. ! Private preferred manufactories With benefits in obtaining loans and tax benefits. Private royal manufactories with various privileges ^ 01 02 03 04 Ordinary, unprivileged manufactories The development of which was small, as they did not enjoy any patronage of the state. B France became a European supplier of such goods as: expanding of royal factories • luxury goods and art (Paris), • silk fabrics (Lyon, Trois), • thin cloth (Languedoc), • canvas (Brittany), • glass, lace, sugar, soap, leather, etc End of the 17th, early 18th centuries France was in a state of economic and political decline caused by the feudal crisis. In the 18th century France suffered a number of defeats in the wars and lost some of its colonies. Primary accumulation of capital in Germany Germany's economic development had significant successes, expressed economic development of Germany in the progress of agriculture, the high development of crafts and trade, and the increase in the population Has reached a high level: weapons production The development of jewelry and . engraving mining industry • led to the decline of North German and South German cities Economic decline • to the fall of trade and the crisis of the craftfall of trade and the crisis of the craft • increased feudal exploitation • Hamburg became the main center of the German bread trade, and Ganza broke up Its political fragmentation played a significant role in the economic decline of Germany in the 16th century. The Thirty Years' War of 1618-1648 As a result, the isolation of the geographical area was added to the economic isolation. • From the second half of the 18th century in eastern Germany began XVIII year’s outcomes to strengthen the principality brandenburg. • In the 18th century Prussia became a strong and peculiar militarypolitical monarchy, using violent military methods of exploitation of peasants. Thank you! Презентация студентов РЭУ им. Плеханова, Беспрозванных Сергея и Кемала Аманмурадова, группы 15.06Д-Э01.20Б