УТВЕРЖДАЮ: Директор ЯСКТ С.В.Калинина «____»______2014
реклама
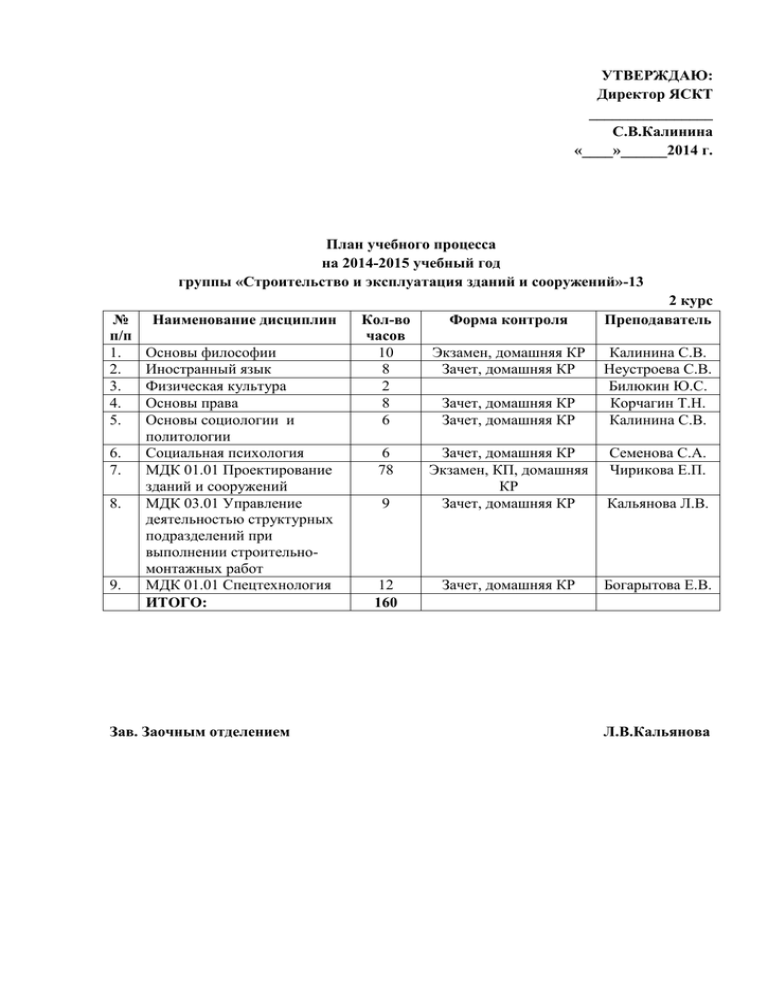
УТВЕРЖДАЮ: Директор ЯСКТ ________________ С.В.Калинина «____»______2014 г. План учебного процесса на 2014-2015 учебный год группы «Строительство и эксплуатация зданий и сооружений»-13 № п/п 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Наименование дисциплин Основы философии Иностранный язык Физическая культура Основы права Основы социологии и политологии Социальная психология МДК 01.01 Проектирование зданий и сооружений МДК 03.01 Управление деятельностью структурных подразделений при выполнении строительномонтажных работ МДК 01.01 Спецтехнология ИТОГО: Зав. Заочным отделением Кол-во часов 10 8 2 8 6 6 78 9 12 160 Форма контроля Экзамен, домашняя КР Зачет, домашняя КР Зачет, домашняя КР Зачет, домашняя КР 2 курс Преподаватель Калинина С.В. Неустроева С.В. Билюкин Ю.С. Корчагин Т.Н. Калинина С.В. Зачет, домашняя КР Экзамен, КП, домашняя КР Зачет, домашняя КР Семенова С.А. Чирикова Е.П. Кальянова Л.В. Зачет, домашняя КР Богарытова Е.В. Л.В.Кальянова ИНОСТРАННЫЙ ЯЗЫК (Вариант определяется по последней цифре номера зачетной книжки) ВАРИАНТ № 1 1. Read and translate the text. THE UNITED KINGDOM OF GREAT BRITAIN AND NORTHERN IRELAND Great Britain lies on the Atlantic coast of Western Europe, separated from France by only 34 km (21 miles) of water. It is made up of three countries, England, Scotland and Wales. Great Britain with Northern Ireland forms the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. The capital of the United Kingdom is London, in England. Great Britain’s largest island neighbor is Ireland. This is mainly occupied by the independent Republic of Ireland. The remainder is Northern Ireland which is a part of the United Kingdom. Many small islands are also linked with the United Kingdom. Although a small island, Great Britain has a remarkable variety of landscapes. To the north and west are highlands – the mountains of Scotland, Cumbria and Wales, and the Pennine Chain. To the east are flat plains, and in the south are lowlands broken by low ranges of hills. To the Southwest are the bleak moors of Devon and Cornwall. The continent of Europe extends out below the waters of the Atlantic Ocean, in the form of a continental shelf. Great Britain is perched on this shelf, surrounded by the shallow waters of the North Sea, the Irish Sea and the English Channel. A warm ocean current, the Gulf Stream, washes Britain’s western shores. This water heats up and cools down very slowly. Britain therefore enjoys warmer winters and cooler summers than other countries at the same latitude. The west of the island has a higher rainfall and slightly milder climate than the east. Britain has been many centuries in the making. The Romans conquered Britain, but were unable to subdue the independent tribes in the west and the north. Other invaders wee Angles, Saxons, Jutes, Vikings and Normans. England waged numerous colonial wars and was the empire for many centuries. England was the first country where the capitalism was established. Great Britain is a highly developed industrial country. It is known as one of the largest producers and exporters of machinery, electronics, textile, aircraft and navigation equipment. One of the chief industries of the country is shipbuilding. The UK is a constitutional monarchy. The powers of the British Queen are limited by the Parliament. The British Parliament consists of the sovereign, the House of Lords and the House of Commons. 2. Answer the questions. Where does the UK lies? What does the UK consist of? What is Great Britain’s largest island neighbor? What proves that Great Britain has a variety of landscapes? What is Britain’s history? ВАРИАНТ № 2 Read and translate the text. UK POLITICAL SYSTEM The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland is a constitutional monarchy. It means that the government of the United Kingdom is by a hereditary House of Lords. The sovereign has the title of King (or Queen). The Sovereign has very fe w functions that really matter, such as the function of the arbiter of last resort in some matters. These matters can be dissolution of the Parliament and invitations to form a government when there is no clear majority. The Queen is Elizabeth II. The supreme legislative power is vested in the Parliament, which sits for 5 years unless sooner dissolved. The Parliament has two chambers: the House of Lords with about 830 hereditary peers, 26 spiritual peers, about 270 life peers and peeresses, and the House of Commons. The House of Commons has 650 popularly elected members. The House of Commons is the real governing body of the United Kingdom. In order to become a law, a new bill proposed by the Cabinet must be approved by both houses of the Parliament. The Lords cannot veto a bill, but they can delay it for a maximum of one year. Financial bills cannot be delayed by the House of Lords. The executive power of the Crown is exercised by the Cabinet, headed by Prime Minister. Prime Minister, normally the head of the party commanding a majority in the House of Commons, is appointed by the Sovereign. Prime Minister appoints the rest of the Cabinet. All ministers must be members of one or the other houses of Parliament. They are individually and collectively responsible to the Crown and the Parliament. Government in Britain since 1945 has alternated between only two political parties, the Conservatives (the Tory) and the Labor Party. No other party has been in office at all since 1945 and there have been no coalitions. The third long-established party, the Liberals, enjoyed moments of success, but no member of the Liberal party has held government office since 1945. 2. Answer the questions. What does the term “constitutional monarchy” mean? What are the functions of the sovereign? Who are the members of the House of Lords? What are the functions of the houses? What are the functions of Prime Minister and the Cabinet of Ministers? ВАРИАНТ № 3 Read and translate the text. LONDON London is the capital of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. It is the largest city in Europe and one of the largest cities in the world with the population of 11 million people. About a fifth of the total population of the UK lives in the Greater London area, that is in London and its suburbs. London is home for the headquarters of all government departments, Parliament, the major legal institutions and the monarch. It is the country’s business and banking center and the center of its transport network. It contains the headquarters of the national television networks and of all the national newspapers. The original walled city of London founded by Romans was quite small. In the middle ages it did not contain the Parliament o the Royal Court, because it would have interfered with the interests of the merchants and traders who lived there. It was in Westminster, another city outside London’s walls, that these national institutions met. Today, both “cities” are just two areas in Central London. The City is home to London’s main financial organizations. The Royal Exchange, the Stock Exchange and the Bank of England are situated there. During the daytime, nearly a million people work there, but less than 8000 people actually live there. Other well-known areas of London are the West End and the East End. The former is known for its many theaters, cinemas, luxurious hotels and restaurants and expensive shops. The latter is known as the poorer residential area of Central London; the Port of London is situated there. The two districts of London, the City Westminster and the West End are the main tourist attractions in London. Westminster Abbey, the Houses of Parliament, Buckingham Palace and quite a number of world-famous museums are all located in this area. There are many other parts of central London which have their own characteristics, and Central London itself makes up only a very small part of Greater London. The majority of Londoners live in its suburbs, millions of them traveling into the centre each day to work. These suburbs cover a vast area of land. London is a cosmopolitan city. People of several races and many nationalities live there. A survey carried out in the 1980-ies found that 137 different languages were spoken in the homes of just one district of London. 2. Answer the questions. What is the population of London? What part does London play in the life of the United Kingdom? What is the history of Westminster and the City of London? What are the West End and the East End known for? What is the main tourist attraction in London? ВАРИАНТ № 4 Read and translate the text. CITIES OF THE UNITED KINGDOM The population of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland is more than 57 million people. It is mostly urban: nine tenth of it lives in towns and cities. London, the largest city in Europe, dominates Britain. It is home for the headquarters of all government departments, Parliament, the major legal institutions and the monarch. It is the country’s business and banking center and the centre of its transport network. It contains headquarters of the national television networks and of all the national newspapers. It is about 7 times larger than any other city in the country. About a fifth of the total population of the United Kingdom lives in the Greater London area. The country’s second largest city is Birmingham. During the industrial revolution, the city and the surrounding area of the west midlands, known as the Black country, developed into the country’s major engineering centre. Factories of Birmingham still convert iron and steel into a vast variety of goods. In northern England, there are large deposits of coal and iron ore. They enabled this area to lead the industrial revolution in the 18th century. On the western side, the Manchester area became, in the 19th century, the world’s leading producer of cotton goods. On the eastern side, towns such as Bradford and Leeds became the world’s leading producers of woolen goods. Further south, Sheffield became a center for the production of steel goods. Further north, around Newcastle, shipbuilding is the major industry. Glasgow in Scotland is the third largest city in Britain. It is associated with heavy industry and some of the worst housing conditions in Britain. However, this image is one-sided. Glasgow has a strong artistic heritage. At the turn of the last century, the work of the Glasgow school put the city at the forefront of English design and architecture. Edinburgh, which is half the size of Glasgow, is the city of science and is associated with science, law and administration. This reputation, together with many historic buildings has led to its being called “The Athens of the North”. The annual festival of the arts is internationally famous. 2. Answer the questions. What is the population of the United Kingdom? What part does London play in the life of the United Kingdom? What is Birmingham noted for? What natural resources are thee in northern England? What is Edinburgh associated with? ВАРИАНТ № 5 Read and translate the text. THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA The United States of America are situated in the central part of the North American continent. Its western coast is washed by the Pacific Ocean and its eastern coast – by the Atlantic Ocean. The total area of the USA is over nine million square kilometers. The population of the USA is about 250 million people; most of the population lives in towns and cities. The USA is a very large country, so it has several different climatic regions. The coldest regions are in the north and north-east. The south has a subtropical climate. The United States is a land of rivers and lakes. The northern state of Minnesota is a land of 10 000 lakes. The longest rivers in the USA are the Mississippi, the Missouri and the Rio Grande. The highest mountains are the Rocky Mountains, the Cordillera and the Sierra Nevada. The United States is rich in natal and mineral resources. It producers copper, oil, iron ore and coal. It is a highly-developed industrial and agricultural country. There are many big cities in the USA, such as New York, Chicago, Los Angeles, Philadelphia and others. The national capital is Washington, D.C. Its population is about 3,4 million people. Washington was built in the late eighteenth century as the center of government. It was named after George Washington. The USA became the world leading country at the beginning of the twentieth century. 2. Answer the questions. What can you say about the geographical position of the United States of America? What is the total area and the population of the United States? What is the climate of the United States like? Why is the United States called a land of rives and lakes? What are the major cities of the United States? ВАРИАНТ № 6 Read and translate the text. US GOVERNMENT The USA is a presidential republic. The legislative branch of the US Government, or the Congress, represents all the American States. It consists of two parts: the House of Representatives and the Senate. Each state has two senators, who are elected every 6 years. A senator must be at least 30 years old, a citizen of the United States for 9 years, and live in the state she or he will represent. A representative must be at least 25 years old, a citizen for 7 years, and live in the state. The job of the Congress is to make laws. The President can veto a bill. The Congress can pass the law anyway if it gets a two-thirds majority vote. The Congress can also declare war. The House of Representatives can also impeach the President. This means that the House can charge the President with a crime. In this case, the Senate will put the President appoint5s to the Supreme Court. The executive branch of the government puts the country’s laws into effect. The President of the United States is a member of the executive branch. The President must be at least 35 years old, and be a natural citizen of the USA. In addition, he must have lived in the US for at least 14 years, and be a civilian. The President is elected every four years and cannot serve more that two terms. The Vice-President of the USA is president of the Senate. When the President receives a bill from the Congress, he must sign it, and then the bill becomes a law. However, if he disagrees with the law, he can veto it. The President can also ask the Congress to declare war. He also appoints the justices to the Supreme Court. He must do his job according to the Constitution, or may be impeached. The judicial branch of the government is the system of courts in the United States. Its job is to enforce laws. The Supreme court is the highest court in the country. It consists of 9 justices: one Chief Justice and 8 associate justices. The President appoints the justices are appointed for life. The Supreme Court makes sure that people obey the laws. The Supreme Court can also decide if a law is constitutional, that is, if it is in agreement with the Constitution. The judicial branch works together with the legislative and executive branches to protect the Constitution and the rights of people. 2. Answer the questions. What is the legislative branch of the US government? Who can be elected a senator? What are the jobs of the Congress? What can and must the President do? How are the justices of the Supreme court appointed? ВАРИАНТ № 7 Read and translate the text. WASHINGTON, D.C. The United States is a federal union which is made up of fifty states and one independent district – the District of Columbia. The District of Columbia is the territory of the national capital of the USA, Washington, with its own laws and regulations. Washington, D.C. is situated on both banks of the Potomac river, between the two states, Maryland and Virginia. This place was chosen by the first American President George Washington. The plot of land of a hundred square miles was bought from private owners by the state. In 1790 George Washington laid the corner-stone of the Capitol Where the Congress sits. The place was called the District of Columbia in honor of Columbus, the discoverer of America. The capital got the name of Washington after the name of its founder. Washington has been the federal capital since 1800. Washington is sometimes called the heart of America. It is the place where the federal government works and where each President of the United States lives. Washington is smaller in size than the largest cities of the USA, such as New York, Chicago, Detroit or Los Angeles. The population of Washington is about 1 million people. The buildings in Washington are not very tall because no building must be taller than the Capitol. But in political sense Washington is the centre of the country and the most important city of the United States. 2. Answer the questions. How many parts is the USA made up of? What is the District of Columbia? How was Washington, D.C. founded? What is Washington famous for? In what sense is Washington the most important city in the USA? ВАРИАНТ № 8 Read and translate the text. NEW YORK New York is one of the largest cities in the world. It was founded three hundred years ago at the mouth of the Hudson river. The centre of New York is Manhattan Island. In 1626 it was bought from the Indians for a handful of trinkets that cost twenty-four dollars. Today Manhattan is the center of business and finance. Numerous skyscrapers house banks and offices of American business. Broadway begins here, the Stock Exchange is located here too. Very few people live in Manhattan, though the majority work here. Numerous bridges link Manhattan with the opposite shores. New York is inhabited by people of almost all nationalities and races. It is called “modern Babylon”. At the turn of the twentieth century a lot of people came to the USA from different countries of the world. They entered the USA through New York, the Gateway of America. New York is one of the leading manufacturing cities in the world. The most important indu stries are those producing paper products, vehicles, glass, chemicals, machinery. New York has a heavy traffic. The sea encircles many of the city areas and the ships go over or under New York traffic routes. 2. Answer the questions. When was New York founded? What is the centre of the city? Why is New York called “modern Babylon”? What are the most important industries in New York? ВАРИАНТ № 9 Read and translate the text. THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA The United States of America are the forth largest country in the world (after Russia, Canada and China). It occupies the southern part of North America and stretches from the Pacific to the Atlantic Ocean. The total area of the country is about nine and half million square kilometers. The USA borders on Canada in the north and on Mexico in the south. It also has a sea-border with Russia. The USA is made up of 50 states and the District of Columbia, a special federal area where Washington, the capital of the country, is situated. The population of the country is about 250 million. If we look at the map of the USA, we can see lowlands and mountains. The highest mountains are the Rocky Mountains, the Cordillera and the Sierra Nevada. The highest peak is Mount McKinley which is located in Alaska. America’s largest rivers are the Mississippi, the Missouri, the Rio Grande and the Columbia. The Great Lakes on the border with Canada are the largest and the deepest in the USA. The climate of the country varies greatly. The coldest regions are in the North. The climate of Alaska is arctic; the climate of the central part is continental; the south has a subtropical climate. Hot winds blowing from the Gulf of Mexico often bring typhoons. The climate along the Pacific coast is much warmer than that of the Atlantic coast. The USA is a highly developed industrial country. It is the world’s leading producer of copper and oil and the world’s second producer of iron ore and coal. Among the most important manufacturing industries are aircraft, cars, textiles, radio and televisions sets, armaments, furniture and paper industries. Though mainly European and African in origin, Americans are made up of nearly all races and nations, including Chinese and native Americans. The largest cities of the USA are: New York, Los Angeles, Chicago, Philadelphia, Detroit, San Francisco, Washington and others. The USA is a federal union of 50 states; each of them has its own government. The seat of the central (federal) government is Washington, D.C. According to the US Constitution, the government is divided into three branches: the executive branch headed by the President, the legislative, branch exercised by the Congress, and the judicial branch. The Congress consists of the Senate and the House of Representatives. There are two main political parties in the USA: the Republican and the Democratic. 2. Answer the questions. What territory does the USA occupy? What is the USA made of? What are the rivers and lakes of the USA? How can you characterize the economy of the USA? What is the political system of the USA? ВАРИАНТ № 10 Read and translate the text. US POLITICAL SYSTEM The USA is a presidential republic. The legislative power of the USA is vested in the Congress of the USA. The Congress was created by Article I of the Constitution, adopted in 1787. It consists of two chambers – the Senate and the House of Representatives. The Senate is made up of 100 members (2 from each state), elected for a term of 6 years. One third of the Senate is elected every 2 years. To be elected a Senator, a person must be at least 30 years old and have been the citizen of the USA for at least 9 years. The House of Representatives comprises representatives from each state, elected for a two-year term. The number of representatives from each state depends on its population, but every state is represented. To be elected a representative, a person must be at least 25 years of age and have been a citizen of the USA for at least 7 years. The presiding officer of the Senate is the Vice-President of the USA. The presiding officer of the House of Representatives, the Speaker, is elected by the house. The work of preparing and considering laws is done by the committees of both Houses. There are 15 standing committees in the Senate and 19 in the House of Representatives. The Congress assembles at least once a year. The executive branch of the government consists of the President, the Vice-President and the Cabinet. The President’s term of office is four years, together with the Vice-President, chosen for the same term. The President is the head of the executive branch of the government; he appoints the members of the Cabinet. The Cabinet advises the President on many matters and is composed of the heads of ten executive departments: Secretary of State, Secretary of Treasury, Secretary of Defense and others. The judicial branch of the government is headed by the Supreme Court which settles disputes between the states. The Supreme Court may veto any law passed by the Congress if it contradicts the Constitutions of the USA. The United States is a federal Union, and the President is the head of the Federal government which deals with international problems and national matters. But every state has its own constitution and the state government headed by the Governor and managing their local affairs. Their laws and decisions must not contradict the Constitution of the USA. The US national flag – Stars and Stripes – is red, white and blue. Thirteen stripes represent the original 13 states of the US; the 50 stars represent the current number of states. 2. Answer the questions. What is the legislative power in the USA vested in? What kind of person may be elected a senator? How is a representative elected? Who are the presiding offices of the Senate and the House of Representatives? What does the US national flag represent? ОСНОВЫ СОЦИОЛОГИИ И ПОЛИТОЛОГИИ (Вариант определяется по последней цифре номера зачетной книжки) Часть 1. Социология. 1. Предмет и методы социологии. 2. Социальная стратификация. 3. Методы социологического исследования. Генеральная и выборочная совокупность. 4. Семья как социальный институт. 5. История развития социологии. 6. Социальные конфликты, управление конфликтом. 7. Типология обществ, основные законы. 8. Формирование социальных отношений. 9. Социальные институты. 10. Социальный прогресс 11. Культура - распространение, значение творческих личностей. Культурное развитие и деградация. 12. Этнические общности. 13. Личность как субъект и продукт социальных отношений. 14. Социализация-определение, характеристика периодов. 15. Формирование социальных отношений: социальное действие и взаимодействие. 16. Личность в системе социальных отношений (Человек, Личность, Индивид). 17. Генезис семьи: изменения ее внутренней структуры и функций, причины изменений. 18. Предсказуемость общества – социальное последствие институционализации. 19. Изменения стратификации и эволюция классов в России. 20. Девиации - отклоняющееся поведение. Делинквенция - нарушение закона. Часть 2. Политология. 1. История становления политической науки. 2. Методы политических исследований. 3. Политическая мысль в России. 4. Политическая власть - определение, структура, эволюция, легитимность. 5. Формы правления. 6. Политический режим - определение, структура, типы. 7. Демократия. Теории и принципы. 8. Политическая система общества. 9. Государство. Концепции - договорное, силовое, правовое государства. 10. Президент и парламент 11. Партии и партийные системы. 12. Политические институты. 13. Политическая элита и лидеры 14. Политическая культура. 15. Международные отношения. 16. Международные отношения и внешняя политика. 17. Предмет изучения политологии. 18. Международные конфликты - источники, причины и способы их разрешения. 19. Соотношение правового государства и гражданского общества. 20. Политические интересы социальных групп общества. Столкновение интересов как основа политических конфликтов и кризисов. ОСНОВЫ ПРАВА (Вариант определяется по последней цифре номера зачетной книжки) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. Правовое государство. Концепции происхождения государства. Разделение власти. Правонарушение и юридическая ответственность. Правовой статус судебной власти в РФ. Правовые основы государственной службы. Материальная ответственность сторон трудового договора. Разрешение трудовых споров. Законодательство об охране окружающей среды. Цели наказания за совершение преступления. Виды наказаний. Государство как субъект международного публичного права. Правовая и политическая культура. Гражданство в РФ. Понятие и принципы избирательного права. Избирательные системы. Министерство внутренних дел РФ и его органы. Министерство юстиции РФ. ОСНОВЫ ФИЛОСОФИИ (Вариант определяется по последней цифре номера зачетной книжки) 1. Соотношения Знания и Мудрости в философии. 2. Учение Сократа о нравственности. 3. Эпикур и его учение о Счастье. 4. Значение трудов Декарта для науки и философии. 5. Моральная философия Канта. 6. Гегель о смысле человеческой истории. 7. Философия пессимизма Шопенгауэра. 8. Основные идеи философии Ницше. 9. Философия творчества Н.А.Бердяева. 10. Учение о Человеке в философии экзистенциализма. 11. Основополагающие категории человеческого бытия. 12. Психофизическая проблема в науке и философии, ее современная интерпретация. 13. Сознание, мышление, язык. 14. Сознательное и бессознательное. Основные идеи психоанализа Фрейда и Юнга. 15. Пространство и Время в современной научной картине мира. 16. Проблема «Конца Истории». 17. Соотношение Веры и Знания в истории человеческой мысли и в настоящее время. 18. Основные функции искусства. Искусство и творение мира. 19. Кризис современной цивилизации и попытка его глобального преодоления. ПРОЕКТИРОВАНИЕ ЗДАНИЙ И СООРУЖЕНИЙ Перечень тем: 1. Строительные материалы и изделия: Основные свойства строительных материалов. Природные материалы. Древесина и материалы из нее. Естественные каменные строительные материалы. Искусственные материалы. Керамические материалы и изделия. Металлические сплавы и изделия из них. Стекло и другие материалы из минеральных расплавов. Минеральные вяжущие вещества. Цементные бетоны. Строительные растворы. Железобетон и железобетонные изделия. 2. Основы проектирования строительных конструкций: Классификация строительных конструкций и требования к ним. Основы расчета строительных конструкций и оснований (по предельным состояниям). Нагрузки и воздействия. Конструктивная и расчетная схема. Основы расчета строительных конструкций, работающих на сжатие, на растяжение, на изгиб. Расчет и конструирование соединений строительных конструкций. Основания и фундаменты. 3. Архитектура жилых и общественных зданий и сооружений: Общие сведения о жилых и общественных зданиях и сооружениях. Виды гражданских зданий и их конструктивные элементы. Физико-технические основы проектирования зданий и их ограждающих конструкций. Объемно-планировочные и конструктивные решения гражданских зданий. Многоэтажные каменные, крупноблочные и панельные дома. Большепролетные конструкции покрытий общественных зданий. Специальные конструкции общественных зданий. Градостроительство, функциональное зонирование городской территории. Генпланы жилых и общественных зданий. 4. Архитектура промышленных зданий и сооружений: Виды промышленных зданий, их классификация, требования, предъявляемые к промышленным зданиям. Общие принципы объемно-планировочных и конструктивных решений промышленных зданий. Особенности модульной координации, унификации и типизации в промышленном строительстве. Единая модульная система. Общие принципы проектирования конструктивных элементов промышленных зданий. Фундаменты. Железобетонные и металлические конструкции одноэтажных промышленных зданий. Стены и перегородки. Ограждающие конструкции промышленных зданий. Покрытия промышленных зданий. Естественное освещение, окна и фонари промышленных зданий. Конструкции многоэтажных зданий. Генпланы промышленных зданий. СОЦИАЛЬНАЯ ПСИХОЛОГИЯ Темы контрольных работ: Основные принципы делового этикета. Искусство комплимента. Элементы делового этикета: публичная речь, ее особенности. Элементы делового этикета: деловые приемы. Цель и назначение деловых приемов. Виды приемов. Требования этикета к подготовке и организации делового приема (помещение, украшение стола, сервировка и т.п.). Дресс-код для различных видов приемов. Приглашения на официальные приемы и правила оформления приглашений. Правила рассада за столом. Правила использования на деловых приемах фото- и видеоаппаратуры. 5. Этикет трудоустройства и прохождения собеседования. Требования к оформлению резюме. Стиль деловего резюме. Требования к внешнему виду соискателя. 6. Стресс, его сущность и функции. 7. Основные теории личности в психологии. 8. Роль семьи и наследственности в формировании индивидуальности человека. 9. Общение как социальная деятельность. 10. Конфликты и пути их разрешения. 11. Проблема межличностных отношений в различных сферах деятельности человека. 12. Социально-психологические механизмы общения. 1. 2. 3. 4. ТЕХНИЧЕСКАЯ МЕХАНИКА (Вариант определяется по последней цифре номера зачетной книжки) Студент решает обе задачи, исходные данные для задачи взять из таблиц и схем согласно своему варианту. ЗАДАЧА 1. Для ступенчатого стального бруса требуется: а) определить значение продольной силы и нормального напряжения по длине бруса; б) построить эпюры Ν и σ; в) определить абсолютное удлинение (укорочение) бруса. Модуль продольной упругости Е=2*105 МПа. Данные для задачи своего варианта взять из табл. 4. и схемы на рис. АРХИТЕКТУРА ЗДАНИЙ Контрольная работа состоит из десяти вариантов. Каждый вариант контрольной работы содержит три вопроса. Вариант контрольной работы определяется по последней цифре шифра-номера зачетной книжки студента (при окончании номера на 0—вариант № 10, при цифре 1—№ 1 и т.д.). При выполнении контрольной работы необходимо соблюдать следующие требования: - изложение текстового материала должно быть выполнено технически грамотным языком, в сжатой конкретной форме, не допускается сокращение слов; - чертежи узлов выполняются на листах формата А4 в соответствии с ГОСТами ЕСКД, СПДС. На каждой странице оставляется поля шириной 3-4 см для замечаний проверяющего работу. За ответом на последний вопрос приводится список используемой литературы, ставится подпись исполнителя и оставляется место для рецензии. На обложке тетради указывается учебный шифр, наименование дисциплины, курс, отделение, индекс учебной группы; фамилия, имя, отчество исполнителя. После получения прорецензированной работы студенту необходимо исправить отмеченные ошибки, выполнить все указания преподавателя, повторить недостаточно усвоенный материал. Незачтенные контрольные работы подлежат повторному выполнению. ВАРИАНТ 1. 1. Основные элементы и конструктивные схемы гражданских зданий. 2. Лестницы, их основные элементы и конструктивные решения. 3. Выполнить узлы крепления стеновых панелей к колоннам каркаса. ВАРИАНТ 2. 1. Сечения ленточных фундаментов гражданских зданий в зависимости от климатических и геологических условий. 2. Каркасно-панельные здания и их конструкции. 3. Выполнить узлы опирания лестничных маршей на лестничную площадку. ВАРИАНТ 3. 1. Ленточные фундаменты гражданских зданий, их конструктивные решения. 2. Конструкция скатных крыш, устройство наслонных стропил. 3. Выполнить узлы вертикального и горизонтального стыков крупнопанельных зданий. ВАРИАНТ 4. 1. Столбчатые, сплошные фундаменты гражданских зданий, их конструктивные решения. 2. Совмещенные покрытия гражданских зданий. 3. Выполнить узлы опирания ригеля на колону в каркасно-панельном здании. ВАРИАНТ 5. 1. Стены из кирпича, классификация, конструктивные решения. 2. Стыки конструкций каркасных зданий. 3. Выполнить узлы перемычек над проемами в несущей и ненесущей кирпичной стене. ВАРИАНТ 6. 1. Перекрытия гражданских зданий, их классификация, конструктивные решения. 2. Стены из мелких блоков, легкобетонных и ячеистобетонных камней. 3. Выполнить узлы фундаментов каркасно-панельных зданий. ВАРИАНТ 7. 1. Перегородки, их классификация. Конструктивные решения кирпичных, панельных перегородок и перегородок из мелких плит. 2. Свайные фундаменты гражданских зданий, их конструктивные решения. 3. Выполнить узлы парапета кирпичного здания при совмещенном покрытии. ВАРИАНТ 8. 1. Полы и их конструктивные решения. 2. Конструктивные схемы крупнопанельных зданий. Конструкции стеновых панелей. 3. Выполнить узлы свайных фундаментов для кирпичных и крупнопанельных зданий. ВАРИАНТ 9. 1. Окна и двери, их конструктивные решения. 2. Стыки стеновых панелей крупнопанельных зданий. 3. Выполнить узел парапета кирпичного здания с чердачным покрытием. ВАРИАНТ 10. 1. Виды покрытий, конструкции скатных крыш. 2. Деформационные швы. Отдельные опоры. Перемычки. 3. Выполнить узлы ленточных фундаментов для кирпичных и крупнопанельных зданий. СПИСОК ЛИТЕРАТУРЫ 1. Буга П.Г. Гражданские, промышленные и сельскохозяйственные здания. –М., 1987. 2. Благовещенский Ф.А., Букина Е.Ф. Архитектурные конструкции. –М., 1985. 3. Архитектурные конструкции/ Под ред. З.А.Казбек-Казиева. –М., 1986. 4. Неелов В.А. Гражданские здания. –М., 1988. 5. Конструкции гражданских зданий/ Под ред. Т.Г.Маклаковой. –М., 1986. 6. Шерешевский И.А. Конструирование гражданских зданий. –М., 1981. 7. Шерешевский И.А. Конструирование промышленных зданий и сооружений.—М., 1980. 8. Трепененков Р.И. Альбом чертежей конструкций и деталей промышленных зданий. – М., 1980. 9. Неелов В.А. Промышленные и сельскохозяйственные здания. –М., 1980. 10. СНиП 2.01.07-85*. Нагрузки и воздействия. 11. СНиП 2.02.01-83*. Основания зданий и сооружений. 12. СНиП 2.01.01-82. Строительная климатология и геофизика. 13. СНиП П-7-81*. Строительство в сейсмических районах. 14. СНиП 2.02.04-88. Основания и фундаменты на вечномерзлых грунтах. 15. СНиП 2.07.01-89*. Градостроительство. Планировка и застройка городских и сельских поселений. 16. СНиП 2.08.01-89*. Жилые здания. 17. СНиП 2.08.02-89*. Общественные здания и сооружения. 18. СНиП 2.09.02-85*. Производственные здания. 19. СНиП 2.09.03-85. Сооружения промышленных предприятий. 20. СНиП 2.11.01*-85. Складские здания. 21. СТ СЭВ 3977-83. Здания производственных промышленных предприятий. Основные положения проектирования. 22. СТ СЭВ 3976-83. Здания жилые и общественные. Основные положения проектирования. ФИЗИЧЕСКАЯ КУЛЬТУРА Перечень тем: 1. Физическая культура в профессиональной подготовке студентов и социокультурное развитие личности студента. Легкая атлетика: 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Бег на короткие дистанции. Прыжок в длину с места. Бег на короткие дистанции. Прыжки в длину способом «согнув ноги». Бег на средние дистанции. Бег на длинные дистанции. Бег на короткие, средние и длинные дистанции. Баскетбол: 7. Техника выполнения ведения мяча, передачи и броска мяча в кольцо с места. 8. Техника выполнения ведения и передачи мяча в движении, ведение – 2 шага – бросок. 9. Техника выполнения штрафного броска, ведение, ловля и передача мяча в колоне и кругу, правила баскетбола. 10. Совершенствование техники владения баскетбольным мячом. Волейбол: 11. Техника перемещений, стоек, технике верхней и нижней передач двумя руками. 12. Техника нижней подачи и приёма после неё. 13. Техника прямого нападающего удара. Техника изученных приёмов. 14. Совершенствование техники владения волейбольным мячом. 15. Техника попеременного двухшажного хода. Техника подъёмов и спуска в «основной стойке». 16. Техника одновременного бесшажного и одношажного ходов, подъёмов «полуёлочкой» и «ёлочкой». 17. Техника поворота «переступанием», «плугом». Техника перехода с хода на ход. 18. .Совершенствование техники перемещения лыжных ходов. Гандбол: 19. Техника владения мячом на месте. Стойка вратаря, удары по воротам. 20. Техника владения мячом в движении. Тактика игры в гандбол. 21. Техника владения мячом. Перемещения, передачи мяча, броски по воротам. 22. Совершенствование техники владения гандбольным мячом.